Filter
902
Featured
43
25
Language
Document type
320
117
115
81
56
53
52
30
26
12
10
10
10
7
3
Countries / Regions
228
36
28
19
11
10
8
8
7
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
117
67
39
9
5
3
2
Overview and Practical Experiences from Ethiopia and Uganda. Slide set.
This webinar provides an overview of the new IEC & Social Mobilization NTD Tool Kit, which leads users through a step-by-step process to systematically review, revise, develop and adapt current IEC materials and social mobiliza
...
Dengue is a mosquito-borne viral disease that has rapidly spread to all regions of WHO in recent years. Dengue virus is transmitted by female mosquitoes mainly of the species Aedes aegypti and, to a lesser extent, Ae. albopictus. These mosquitoes are also vectors of chikungunya, yellow fever and Zik
...
Gambiense human African trypanosomiasis is a deadly infectious disease affecting West and Central Africa, South Sudan and Uganda, and transmitted between humans by tsetse flies. The disease has caused several major epidemics, the latest one in the 1990s. Thanks to recent innovations such as rapid di
...
Since 1996, trachoma has been targeted for elimination as a public health problem worldwide. The active trachoma criterion for national elimination as a public health problem is a TF1–9 < 5%, sustained for at least two years in the absence of antibiotic mass drug administration (MDA), in each formerly endemic EU. Usi
...
The leishmaniases are a group of diseases caused by Leishmania spp., which occur in cutaneous, mucocutaneous and visceral forms. They are neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), which disproportionately affect marginalized populations who have limited access to health care. HIV co-infected patients with
...
2nd edition. These guidelines include several notable changes from the first edition. For cutaneous leishmaniasis, ketoconazole has been removed from the list of treatment options; the number of Leishmania species for which there is strong evidence for the efficacy of miltefosine has increased from
...
The main purpose of the meeting was to review tsetse control tools, activities and their contribution to the elimination of gHAT and the monitoring thereof. Seven endemic countries provided reports on recent and ongoing vector control interventions at the national level (Angola, Cameroon, Côte d’
...
Tis first edition describes the standard operating procedures for health products for NTDs amenable to preventive chemotherapy and the medicines donated to treat them. These include albendazole for lymphatic filariasis and soil-transmitted helminthiases; azithromycin for trachoma and yaws; diethylca
...
Noma (cancrum oris) is a serious gangrenous disease of the mouth and face, mainly affecting children aged 2 to 6 years in sub-Saharan Africa.
Despite substantial knowledge gaps, it is reported to be linked with malnutrition, poor oral hygiene, immunosuppression, and living in extreme poverty situ
...
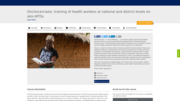
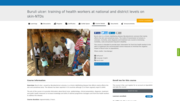
Onchocerca volvulus transmitted by repeated bites of infected blackflies (Simulium spp.). These blackflies breed along fast-flowing rivers and streams, close to remote villages located near fertile land where people rely on agriculture.
There is a need to reinforce skills of national and district
...
This document sets out, therefore, to explain the socioeconomic value of investing in the fight against NTDs and highlights priorities for global investment attention. Our work was guided by the need not only for
additional funding and funders but also for the need to understand the current funding
...
Overview
The aim of this guide is to support national immunization programme managers and others responsible for implementing human rabies vaccine programmes to:
inform policy discussions and operational planning for introducing or expanding rabies post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) into a nationa
...
This course is intended to provide basic information for front-line health workers to be able to implement the recommended control measures to minimize the negative impact of Buruli ulcer on populations.
In 2013, WHO and the Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics convened a meeting of Buruli ulcer experts in Geneva, Switzerland (9) at which two priority unmet needs in diagnosis were identified:
a diagnostic test for early detection of Buruli ulcer in symptomatic patients with sufficient positive
...
Key facts
Buruli ulcer is a chronic debilitating disease caused by an environmental Mycobacterium ulcerans.
At least 33 countries with tropical, subtropical and temperate climates have reported Buruli ulcer in Africa, South America and Western Pacific regions.
It often affects the skin an
...
Principaux faits
L’ulcère de Buruli est une infection chronique débilitante causée par la bactérie Mycobacterium ulcerans.
L’ulcère de Buruli a été signalé dans au moins 33 pays situés dans des régions au climat tropical, subtropical ou tempéré d’Afrique, d’Amérique
...
Datos y cifras
La úlcera de Buruli es una enfermedad crónica y debilitante causada por una micobacteria ambiental: Mycobacterium ulcerans.
Al menos 33 países de clima tropical, subtropical o templado han notificado casos de úlcera de Buruli en África, América del Sur y las regiones
...
Parasites & Vectors volume 15, Article number: 389 (2022)
Dengue is one of the common arboviral infections and is a public health problem in South East Asia. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to evaluate the prevalence and distribution of dengue in SAARC (South Asian Associ
...