Filter
394
Text search:
Schistosomiasis
Featured
44
98
Language
Document type
177
107
42
25
17
8
6
4
2
2
1
1
1
1
Countries / Regions
35
14
13
12
12
11
10
7
7
7
7
6
6
5
5
5
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
136
57
37
28
16
10
7
Toolboxes
96
35
16
9
9
8
7
6
4
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
Despite pandemic-related disruptions, a total of 76.9 million people received treatment for schistosomiasis in 2020, representing a global coverage of 31.9%, compared with 105 million treated in 2019 (coverage of 44.8%).
The latest data published
...
Clin Microbiol Infect 2010; 16: 225–231 Abstract In non-endemic countries, acute (invasive) schistosomiasis (AS) is typically seen in non-immune travellers, whereas chronic schistosomiasis is more
...
HIV-1 infection disproportionately affects women in sub-Saharan Africa, where areas of high HIV-1 prevalence and Schistosoma haematobium endemicity largely overlap. Female genital schistosomiasis (FGS), caused most frequently by S. haematobium egg d
...
The Community Dialogue Approach is a promising social and behaviour change intervention, which has shown potential for improving health seeking behaviour. To test if this approach can strengthen prevention and control of schistosomiasis at community
...
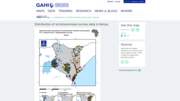
Maps
Maximum point prevalence of schistosome inceftion and location of S. mansoni and S. haematobium surveys.
Websites last accessed on 24.03.2023
A parasite is an organism that lives on or in a host and gets its food from or at the expense of its host. Parasites can cause disease in humans.
Website last accessed on 24.03.2023
A parasite is an organism that lives on or in a host and gets its food from or at the expense of its host. Parasites can cause disease in humans.
DNA studies of Egyptian mummies shows evidence of the existence of Schistosomiasis about 5000 years ago. Schistosomiasis is increasing in prevalence, affecting nearly 10% of the world’s populatio
...
PLoS ONE 13(8): e0202499. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202499
This was a school-based cross-sectional study conducted in 2015 among 305 school children aged 7–16 years from two primary schools located in Ilemela and Magu Districts, north-western Tanzania. Single stool and urine samples w
...
Infographic
Disease: Infection is widespread in poor communities, 221 million people affected worldwide...
Affected Populations: Women, Children...
Prevention and Control: WHO recommends praziquantel for treatment of all forms of schistosomiasis.
...
Species of the genus Schistosoma are digenetic trematodes and the causative agents of the Neglected Tropical Disease (NTD) schistosomiasis; a parasitic disease that ranks second only to malaria in terms of socioeconomic impacts. Over 220 million peo
...
Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia, is an infection caused by a parasitic worm that lives in fresh water in subtropical and tropical regions.
Schistosoma haematobium is a parasitic digenetic trematode responsible for schistosomiasis (also known as bilharzia). The disease is caused by penetration of the skin by the parasite, spread by intermediate host molluscs in stagnant waters, and can
...
Situation Analaysis and Needs Assessment
Coordinated Use of Anthelminthic Drugs in Control Interventions: a Manual for Health Professionals and Programme Managers
Bambo has Bilharzia (English version)
recommended
What Children Should Know About Bilharzia; Educational Comic. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This document was made possible through a financial grant from Merck, Germany. In 2007, Merck entered into a partnership with the World Health Organization (WHO) to combat schis
...
Schistosomiasis, which is the second most important parasitic infection after malaria in terms of its socioeconomic impact, is responsible for the loss of an estimated 4.5 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) worldwide.
...
Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia, is a disease caused by parasitic worms. Although the worms that cause schistosomiasis are not found in the United States, people are infected worldwide. In
...
معلومات ضرورية للأطفال
عن البلهارسيا
Bambo has bilharzia: what children should know about bilharzia. Comic book.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This document was made possible through a financial grant from Merck, Germany. In 2007, Merck entered into a partnership with the World
...