Filter
1103
Text search:
surgical
site
Featured
154
297
Language
Document type
618
215
104
85
24
23
16
11
3
2
1
1
Countries / Regions
106
57
48
35
32
25
24
20
19
18
17
16
16
16
14
13
12
11
11
11
8
8
8
8
7
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
459
195
71
69
45
29
12
1
1
Toolboxes
87
77
69
52
51
43
40
39
36
27
21
16
15
15
14
12
10
6
3
3
1
1
These WHO guidelines which were updated in 2018, are valid for any country and suitable to local adaptations, and take account of the strength of available scientific evidence, the cost and resource implications, and patient values and preferences.
The 2018 edition of the guidelines includes the re
...
During the 17 years since Surgical approaches to the urogenital manifestations of lymphatic filariasis was first published, there has been heightened awareness of the physical, economic and emotional burden of the genitourinary manifestations of fil
...
International Society of Paediatric Surgical Oncology (IPSO) Surgical Practice Guidelines
recommended
ecancer has just published a comprehensive set of guidelines for paediatric cancer surgery, applicable to low and high resource settings across the world. You can read the guidelines online
The guidelines have been developed by the International Society of Paediatric
...
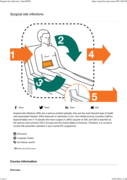
Surgical site infection (SSI) is the most common postoperative complication worldwide. WHO guidelines to prevent SSI recommend alcoholic chlorhexidine skin preparation and fascial closure using tric
...
Saving Lives Through Safe Surgery (SaLTS)
Saving Lives Through Safe Surgery (SaLTS)
The report and an accompanying series of studies show the global uptake of the World Health Organization (WHO) Surgical Safety Checklist in its first ten years since its launch and recommend ways the Checklist can be more effectively used to improve
...
Surgical Care At The District Hospital
recommended
Promotion of the quality of clinical care through the identification, promotion and standardization of appropriate procedures, equipment and materials, particularly at district hospital level.
Surgical site infections (SSI) are a serious problem globally; they are the most frequent type of health care-associated infection (HAI) observed on admission in low- and middle-income countries (LM
...
The manual provides suggestions for implementing the checklist, understanding that different practice settings will adapt it to their own circumstances.
The implementation manual is designed to help ensure that surgical teams are able to implement
...
These guidelines have been extracted from the WHO manual Surgical Care at the District
Hospital (SCDH), which is a part of the WHO Integrated Management Package on Emergency
and Essential Surgical
...
The Lancet Vol.400 (2022) p.17-67-1776. Published:October 31, 2022DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01884-0.
Surgical site infection (SSI) is the most common complication of surgery around
...