Filter
186
Text search:
scabies
Featured
33
57
Language
Document type
103
28
21
14
7
5
5
2
1
Countries / Regions
18
7
6
6
6
6
5
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
71
35
12
9
9
4
Toolboxes
32
14
6
6
6
5
4
4
4
3
3
3
2
2
1
1
1
1
Scabies is a skin infection that is a result of direct skin to skin contact and is primarily mediated by close and extended contact with scabies infested person.
...
Scabies is a global health concern disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations such as refugees and asylum seekers. Greece is a main point of entry in Europe for refugees, but epidemiological data on
...
Several Public Health Services and general practitioners in the Netherlands observed an increase in scabies in the Netherlands. Since individual cases of scabies are not notifiable in the Netherland
...
Human scabies is caused by an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis). The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives an
...
Scabies is an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis). The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs.
...
When a person is infested with scabies mites the first time, symptoms typically take 4-8 weeks to develop after being infested. However, an infested person can transmit scabies, even if they do not
...
Human scabies is a parasitic infestation caused by Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis. The microscopic mite burrows into the skin and lays eggs, eventually triggering a host immune response that leads to intense itching and rash.
...
Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei which burrows into the skin and causes severe itching. Scabies is transmitted by direct skin-to-skin contact or indirectly
...
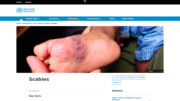
Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin.
The main symptom of scabies is intense itching that's worse at night. It also causes a skin rash on areas wher
...
Scabies is an itchy skin condition caused by a tiny burrowing mite. This eight-legged bug is so small which makes it hard to see on the skin. Approximately 300 million cases of scabies are reported
...
Scabies is caused by Sarcoptes scabiei, a mite which lays its eggs under the surface of your skin and reproduces. When the eggs hatch, mites crawl out onto your skin and make new burrows.
The mites can be difficult to identify and may be confused w
...
The skin of a patient is the first and most visible structure of the body that any health-care worker encounters during the course of an examination. To the patient, it is also highly visible, and any disease that affects it is noticeable and will have an impact on personal and social well-being. Th
...
Available in multiple languages
A dermatologist can often diagnose scabies by visually examining a patient’s skin from head to toe.
To make sure that a patient has scabies, a dermatologist may remove some skin. This is painless
...
The objective of this paper is to summarise and critically review the available data about onchocerciasis in Mozambique, in order to report epidemiological and clinical aspects related to the disease and identify gaps in knowledge. The paper is intended to raise awareness of the existence and import
...