Filter
980
Text search:
Needles
Featured
122
294
Language
Document type
677
138
62
49
14
11
10
10
4
3
2
Countries / Regions
85
48
44
39
35
29
22
19
19
17
16
14
13
13
13
12
12
12
12
11
10
8
8
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
379
128
52
40
27
23
21
1
Toolboxes
169
83
51
42
41
31
31
29
20
15
12
12
12
6
4
4
4
3
3
2
1
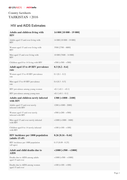
Policy Brief, Updated in March 2017
Reporting period: January 2014 – December 2014
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) epidemic in Myanmar is concentrated among men who have sex with men (MSM), people who inject drugs (PWID) and female sex workers (FSW). HIV prevalence in the adult population aged 15 years and older was esti ...
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) epidemic in Myanmar is concentrated among men who have sex with men (MSM), people who inject drugs (PWID) and female sex workers (FSW). HIV prevalence in the adult population aged 15 years and older was esti ...
ATLAS on substance use (2010)— Resources for the prevention and treatment of substance use disorder
Accessed: 14.03.2019
Q 6. Does the provision of sterile injection equipment to injecting drug users reduce injecting related harm? Is advice on ways to reduce drug related harm safe and effective, using an outreach model of service delivery?
UNAIDS/99.31E (English original, June 1999)
1st revision, April 2000
Accessed: 03.09.2019
Accessed: 29.09.2019
Accessed: 26.09.2019
Accessed: 24.09.2019
Accessed: 04.10.2019
Promising Approaches to Combination HIV Prevention Programming in Concentrated Epidemics
AIDSTAR-One CASE STUDY SERIES May 2010
(pop. 45 782 592)
UNAIDS 2018, Guidance
Indicators for monitoring the
2016 Political Declaration on Ending AIDS
SDG target 3.3: by 2030, end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and neglected tropical diseases and combat hepatitis, waterborne diseases and other communicable diseases.
Technical Paper
Employees, Coworkers, and Supervisors
Accessed: 20.11.2019
2018 Controlling the HIV Epidemic Summit Geneva, 3-4 May 2018
3 May 2018
UNAIDS Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS
30 April 2020
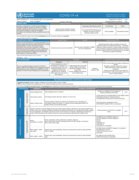
| COVID-19: Essential health services