Filter
1323
Text search:
pollution
Featured
94
276
Language
Document type
485
440
127
68
64
55
20
19
18
9
6
6
4
2
Countries / Regions
125
46
32
29
27
21
21
20
20
17
17
16
16
16
15
14
13
12
12
11
10
10
10
10
10
9
9
9
8
8
8
7
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
434
145
97
42
31
19
5
1
Toolboxes
340
132
90
61
44
34
33
31
31
29
29
17
15
14
14
12
12
10
7
7
6
5
1
1
The Vienna Declaration was signed at the end of the Fifth High-level Meeting on Transport, Health and Environment. The virtual meeting, hosted by the Federal Government of Austria, brought together 46 ministers and representatives of 56 countries in the pan-European region.
The group discussed ho
...
During the first year of the Covid-19 pandemic, the world’s economy slowed. Yet, the global annual average particulate pollution (PM2.5) was largely unchanged from 2019 levels. At the same time, growing evidence shows air
...
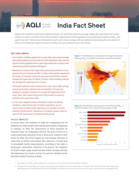
India is the world’s second most polluted country. Air pollution shortens average Indian life expectancy by 5 years,
relative to what it would be if the World Health Organization (WHO) guideline fine particulate
...
Virtually all (99.9 percent) of Southeast Asia’s 656.1 million people live in areas where particulate pollution exceeds the World Health Organization (WHO) guideline of 5 μg/m³. Despite the lockdowns of the pandemic,
...
Bangladesh is the world’s most polluted country. Air pollution shortens the average Bangladeshi’s life expectancy by 6.9 years, relative to what it would be if the World Health Organization (WHO) guideline of 5 μg/m³ was met. Some areas of Ban
...
Pakistan is the world’s fourth most polluted country. Air pollution shortens the average Pakistani’s life expectancy by 3.8 years, relative to what it would be if the World Health Organization (WHO) guideline of 5 μg/m3 was met.1 Some areas of
...
Nepal is the world’s third most polluted country. Air pollution shortens average Nepalese life expectancy by 4.1 years, relative to what it would be if the World Health Organization (WHO) guideline of 5 μg/m3 was met.1 The highest concentrations
...
Globally, environmental pollution and other environmental risks cause 24% of all deaths, and these deaths are largely preventable. A shift towards policies and actions that minimize risks to health and promote health and sustainable personal and soc
...
Despite some improvements, current levels of air pollution still pose a considerable risk to the environment and to human health in the WHO European Region. One issue of concern is that monitoring of particulate matter is very limited in the countri
...
Resource Watch features hundreds of data sets all in one place on the state of the planet’s resources and citizens. Users can visualize challenges facing people and the planet, from climate change to poverty, water risk to state instability, air pollutio
...
European Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences, vol.3 (2016) 1, 192-206
This review shows that if all sub areas of pharmaceutical waste management can efficiently work back to back environmental pollution and dangers to human health ca
...
Sustainable transport systems can protect and promote health, by reducing risks from vehicular air pollution, physical inactivity and traffic injuries, and by providing climate and environmental benefits for urban areas.
We live in a world in which global warming, pollution, social
injustice, inequity and population health fundamentally influence each other. As a result, health and health care can no longer be thought of and practiced in an isolated manner.
WHO has identified climate change as one of the greatest health threats of the 21st century and air pollution as the single largest environmental health risk. Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, chronic resp
...
This report challenges policy-makers and political leaders to tackle fossil fuel production and consumption as a health control issue, in the same way that smoking has been reduced and regulated. Fossil fuel combustion is a major source of toxic air pollut
...
The substantial burden of death and disability that results from interpersonal violence, road traffic injuries, unintentional injuries, occupational health risks, air pollution, climate change, and inadequate water and sanitation falls disproportion
...
Climate risks have significant effects on public health including: injury, death, communicable diseases such as vector-borne and water-borne diseases, and non-communicable impacts such as malnutrition, heat stress and health effects of air pollution
...
Planetary health is a nascent concept focused on the interdependence of human, animal, and environmental health. It offers a new way to solve global problems, such as pollution and global food security, by balancing the health of our planet with hum
...
The report is geared towards mayors, local government officials and city policy planners.It highlights key areas where city leaders can tackle the drivers of NCDs, including tobacco use, air pollution, poor diets and lack of exercise, and improve ro
...
European Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences, vol.3 (2016) 1, 192-206
This review shows that if all sub areas of pharmaceutical waste management can efficiently work back to back environmental pollution and dangers to human health ca
...