Filter
2286
Featured
177
637
Language
Document type
1539
252
177
103
66
50
36
26
13
10
9
3
2
Countries
80
67
64
62
60
59
59
57
54
50
44
39
38
38
37
33
33
30
24
23
22
22
22
21
21
20
20
20
20
18
17
17
16
15
14
14
14
13
12
12
11
11
11
11
11
10
10
9
9
8
8
8
8
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
852
135
88
84
81
60
2
1
1
Toolboxes
312
262
210
114
100
79
74
67
41
39
35
33
29
29
22
19
16
13
12
11
8
6
4
2
1
Problems with education for children with disabilities in Iran“Just Like All Other Kids”: Lack of Access to Inclusive Education for Children With Disabilities in Iran
The government of Kazakhstan has committed to ensuring that children with disabilities have access to inclusive education and it has taken the important step of ratifying international human rights treaties enshrining the rights of people with disabilities, including the right of children with disab
...
Accessed: 30.10.2019
Accessed: 30.10.2019
The Open AIDS Journal, 2012, 6, 245-258
In 2016, Senegal made a minimal advancement in efforts to eliminate the worst forms of child labor. In June, the Government launched an initiative to remove tailbés from the street and prosecute marabouts that perpetrate crimes against their students; however, no marabouts were prosecuted during th
...
The importance of fruits and vegetables in nutritious and healthy diets is well recognized, and in recent years consumers have been encouraged to eat more of these products. For many countries, particularly developing countries, these products have become a valuable commodity. At the same time, food
...
Antimicrobial resistance is a global threat as it is present in all parts of the world and it means that there is a shortage of effective antibiotics to treat simple infections and diseases, also statistics reveal that because of antimicrobial resistance patients’ morbidity and mortality is increa
...
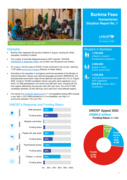
With an FGM prevalence of 75.8% among women aged 15-491, Burkina Faso is classified by UNICEF2 as a ‘moderately high prevalence’ country.
FGM is practised across all regions, ethnic groups and religions in Burkina Faso. There are distinct regional variations; FGM prevalence ranges from 54.8%
...
Event-based surveillance (EBS) is defined as the organized collection, monitoring, assessment and interpretation of mainly unstructured ad hoc information regarding health events or risks, which may represent an acute risk to health. Both indicator-based and event-based surveillance components serve
...
The Suicide Prevention Resource Center (SPRC) has compiled a selection of web pages and information sheets
on mental health and coping with the effects of COVID-19. These resources are a selection from key organizations
in the field. We will continue to update this list as new resources become ava
...
Camp profile focused for the effective and efficient coordination
at camp level; continuity of service monitoring as per the
minimum or sectors’ standard; care and maintenance of the
service provisions; and immediate future planning for bridging
the gaps.
Accessed: 20.04.2020
Across the Western Pacific Region COVID-19 is placing enormous strain on health and economic systems apart from direct threats to personal health safety and livelihood the pandemic also has significant implications on mental health and psychosocial well being adversity is an established risk factor
...
Education is UNESCO’s top priority because
it is a basic human right and the foundation
on which to build peace and drive sustainable
development. UNESCO is the United Nations’
specialized agency for education and the
Education Sector provides global and
regional leadership in education, s
...
This guidance note developed by UNICEF is intended to help WASH staff in their preparedness and response to the current COVID-19 pandemic. It provides an overview of Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) and its intersection with water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH), and how staff can help prevent
...
People experiencing social disadvantage and marginalization are known to be disproportionately impacted by ill-health. In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, persons with disabilities may have increased risk for exposure, complications, and death
Many children will not be ‘safe to learn at home’: As of April 2020, 91 percent of the world’s students have been affected by school closures due to COVID-19. While schools are often places where violence occurs, they also offer a comparatively protective and nurturing space for many children.
...
School health programmes are the most cost-effective way to influence health behaviours in young people. The purpose of this two-part handbook is to support schools as they seek to implement interventions in order to reduce the main modifiable risk behaviours for noncommunicable disea
...
This is a short technical brief with important steps and resources on how country programs can track and address rumors around COVID-19 (as needed). The guide includes a number of great resources and links while also sharing nuggets from global, collective thinking around rumors.
For over a decade, Senegalese and international journalists, human rights advocates, and child protection experts have documented and denounced the ongoing exploitation, abuse and neglect of children living in many of Senegal’s traditional Quranic schools, or daaras. Thousands of these children, k
...
The global COVID-19 pandemic has led to unprecedented levels of disruption to education, impacting over 90% of the world’s student population: 1.54 billion children, including 743 million girls. School closures and the wider socio-economic impacts of COVID-19 on communities and society also disrup
...
Talking About Corona-19
in English and Vietnamese
Informations for Kids
How to respond to, mitigate, and prevent risks to children’s protection and well-being is a profound, if unanswered, question. Practitioners agree that it is necessary to develop or strengthen protective factors at multiple levels, such as the family, community, and national levels.
This report addresses the future of basic education, ICT use in deprived locations, and the use of ICTs in primary school learning in 2020 and 2025, especially in deprived contexts. It draws on research evidence from the literature, the authors’ experiences of ICT use in education initiatives, int
...
The Global Status Report on Preventing Violence Against Children 2020 - Executive Summary
recommended
The report – Global Status Report on Preventing Violence Against Children 2020 – is the first of its kind, charting progress in 155 countries against the “INSPIRE” framework, a set of seven strategies for preventing and responding to violence against children. The report signals a clear need
...
Three billion people – 40 per cent of the world’s population – do not have a place in their homes to wash their hands with water and soap. Three quarters of those who lack access to water and soap live in the world’s poorest countries and are amongst the most vulnerable: children and familie
...
CCC and OECTA Partnership Teaching Resource
Equity and Inclusion: Through the Lens of the Catholic Social Teachings
accessed on 16 July 2020
The principle Life and Dignity of the Human Person is one of the seven themes of Catholic social teaching (United States Conference of Catholic Bishops) . We believe that God created man and woman in his image (Genesis 1:26–27) and because of this all people have inherent dignity . There is nothin
...
The European Commission against Racism and Intolerance (ECRI) was established by the Council of Europe. It is an independent body which ensures respect for human rights in the fight against racism, discrimination (based on "race", ethnic/national origin, colour, nationality, religion, language, sexu
...
23 Dec 2020. The aim of this document is to provide an update on the knowledge surrounding the role of children in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and the role of schools in the COVID-19 pandemic, based on the experience in the EU from August–December, 2020. This document also addresses transmissio
...
The number of confirmed COVID-19 cases detected and reported in each country is influenced by
many factors including limited access and/or utilization of healthcare and COVID-19 testing, limited
surveillance, lack of knowledge amongst the population about when to seek testing, an asymptomatic pres
...
As daily lives and communities are upended by COVID-19, concern is mounting that children’s exposure to violence may increase. Children with a history of abuse may find themselves even more vulnerable – both at home and online – and may experience more frequent and severe acts of violence. Oth
...
Being away from our regular routines and the people we love can be hard. Lost income, crowded living spaces, violence, fear, uncertainty, and living with depression or other mental health problems can make it even harder. We will be living with these difficulties for a long time as we adjust to COVI
...
An estimated 99% of children worldwide – or more than 2.3 billion children – live in one of the 186 countries that have implemented some form of restrictions due to COVID-191. Although children are not at a high risk of direct harm from the virus, they are disproportionately affected by its hid
...
Storybook which is about children's well being and resilience
Somalia WASH Cluster Guidelines
New research explores the stress children in World Vision programmes in the Middle East and Eastern Europe region are under due to COVID-19. In addition to their fear that they themselves or their loved ones will catch the disease, children worry about economic hardships, the loss of their education
...
One booklet is called "Heart-to-Heart with My Child." Published for Rohingya adults and children, it conveys key child protection messages in accessible terms in both Rohingya and in English. The messages are illustrated with embroideries made by Rohingya female artists, engaged with IOM's Rohingya
...
Children living in humanitarian crises face an increased risk of abuse. While the threats of harm are increasing, the established systems in place to protect them are breaking down. Faced with the COVID-19 pandemic and its impacts, vulnerable families suffer multiple hardships. Schools are closed an
...
The report finds that, as of 3 November, in 87 countries with age-disaggregated data, children and adolescents under 20 years of age accounted for 1 in 9 of COVID-19 infections, or 11 per cent of the 25.7 million infections reported by these countries. More reliable, age-disaggregated data on infect
...
UNICEF Annual Report 2017 - Burkina Faso
- Healthcare policy for children
- Food insecurity
- Community health strategy
- National child protection system
etc.
nterim guidance, first issued 25 January 2021, updated 15 June 2021, updated 19 November 2021, updated 23 February 2022, updated 18 August 2022
BMJ Global Health2020;5:e001980. doi:10.1136/bmjgh-2019-00198
Oxfam’s report found that Covid-19 has the potential to increase economic inequality in almost every country at once, the first time this has happened since records began over a century ago. It sets out how a rigged economy is enabling a super-rich elite to amass wealth in the middle of the worst
...
The document presents an assessment developed by both institutions as a contribution to the prioritization of education in national response plans to the health emergency and future recovery strategies. "Countries have deployed various response and recovery plans in which education needs to be incor
...
The INEE Minimum Standards Handbook is the only global tool that articulates the minimum level of educational quality and access in emergencies through to recovery. The Minimum Standards express a commitment that all individuals—children, youth and adults—have a right to education.
There are
...
The Big Idea of the Week delves deeper into a specific COVID-related topic. Each week, Big Idea tackles a specific area of COVID-19 and provides important information, guidelines, and messages for the public.
The Actions for Heroes Guide is developed by the Inter-Agency Standing Committee Reference Group on Mental Health and Psychosocial Support in Emergency Settings (IASC MHPSS RG) to accompany reading the children’s storybook My Hero is You, How kids can fight COVID-19! Available in English, French,
...
6 June 2022
These WHO interim recommendations on the use of the Janssen Ad26.COV2.S (COVID-19) vaccine were developed on the basis of advice issued by the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) and the evidence summary included in the background document referenced below.
Th
...
The United Nations Secretary-General, António Guterres, echoed the concerns of people and organisations around the world when he recently referred to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on schooling as a
‘generational catastrophe’.
.
A Technical Brief for Breakthrough ACTION Field Teams
Modern healthcare has given rise to extremely complex and multifaceted ethical dilemmas. All too often physicians are unprepared to manage these competently. This publication is specifically structured to reinforce and strengthen the ethical mindset and prac
...
On February 29, 2020, the United States and the Taliban signed an agreement outlining a phased withdrawal of US forces from Afghanistan in exchange for Taliban commitments not to allow attacks on the US or its allies from Afghan territory. The troop withdrawal is expected to take place in parallel w
...
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has created a global and gendered crisis that is compounding existing inequalities and disproportionately affecting girls and women. Emerging evidence from the COVID-19 crisis in 2020 shows school closures, disruptions in essential services and rising
...
The strategy recommends that AU Member States should enhance, where feasible, existing COVID-19 surveillance to include:
Community-based surveillance to detect symptomatic cases early for treatment and to avert viral transmission;
Sentinel surveillance in high-risk populations to detect
...
27 September 2022
These WHO interim recommendations for use of the Novavax NVX-CoV2373 vaccine were developed on the basis of advice issued by the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) and the evidence summary included in the background document and annexes referenced below.
Primary Surgery Vol. One: Non-Trauma
recommended
This comprehensive book has established itself as the most useful text for the medical practitioner in poor-resource settings who is obliged to manage surgical cases. It is particularly adapted for those whose surgical experience is basic or minimal. Importantly, it has extensive advice about pitfal
...
Information for policy-makers and planners on conducting deworming as part of an integrated
school health program
Evidence shows that FGM can cause several physical, mental and sexual health complications in girls and women, and in newborns. Health-care providers play an important role in supporting girls and women living with FGM, and improving their health and well-being. They are in a unique position to infl
...
A national faecal examination of 27 729 schoolchildren from 395 schools carried out in
2008 indicated that intestinal parasitic worms affected an estimated five million (56.8%)
children in Kenya. Existing evidence shows that worm infections lead to reduced literacy
levels due to impaired growth a
...
Rural Women Peace Link (RWPL) is a grassroots women-led organization
working in rural areas in the west of Kenya to promote local women’s
involvement in peace building, governance and development.
t aims to enable participants to:
know more about children’s reactions to distress
know what psychological first aid for children is and what it is not
understand the three action principles of ‘Look, Listen and Link’ in relation to children
have practised providing PFA t
...
Terapia interpersonal grupal para la depresión
recommended
a depresión es una afección importante. Es la principal causa de discapacidad en todo el mundo y puede ser causa de suicidio. En este manual se presenta una versión modificada de la terapia interpersonal para la depresión, a fin de que se pueda utilizar en ocho sesiones grupales bajo un formato
...
This manual has been prepared by the Group on Agriculture of the FAO Regional Office for Latin America and the Caribbean. The purpose of this work is to spread the basic concepts of Good Agricultural Practices (GAP)in order to: guide the production systems towards a sustainable agriculture and ecolo
...
This booklet presents key messages for action, summarized from a set of
chapters on different environmental health issues.
A full-scale military attack (invasion) of Ukraine was started by Russia in the night of February 23/24, 2022. Cities, towns and other targets in all regions of Ukraine have been shelled or attacked with rockets, and columns of military vehicles have been invaded the country from three directions (n
...
This booklet presents key messages for action, summarized from a set of chapters on different environmental health issues, available at www.who.int/ ceh/publications/healthyenvironmentsforhealthychildren. The work is a result of an on-going partnership between WHO, UNEP and UNICEF in the area of chi
...
Communications and outreach to policy-makers and the wider public are essential to mobilize and sustain support for policy solutions to air pollution and bring the needed health, environment and economic benefits.
The toolkit provides guidance on where to get started, including the structures and resources that should be put in place at the national and health-care facility level, through a stepwise approach in low-resource settings. As the ultimate goal of an AMS programme is sustainable behaviour change in
...
Large File: 28 MB
Concepte Note, June 2022
first issued 18 August 2022
This brief presents the prospects for sustaining enrollment of Ukrainian students in educational services and addressing accumulating learning losses.
Displacement of Students and Educators. The war in Ukraine has resulted in more than 6
million Ukrainians fleeing to neighboring countries. This in
...
This manual is to assist health care providers and laboratory scientists to diagnose mycobacterium ulcerans disease (Buruli ulcer). The manual aims to achieve a better understanding of the clinical presentation and its diagnosis. The methods described are tailored to various levels of care and avail
...
Buruli ulcer : management of Mycobacterium ulcerans disease : a manual for health care providers
recommended
This manual is addressed to health care providers dealing with Mycobacterium ulcerans disease (Buruli ulcer). The manual aims to achieve a better understanding of the disease, its clinical presentation and its surgical management. The manual is aimed particularly at district health care providers. A
...
Chagas disease (CD) is endemic in the Americas, being present in 21 countries, where it affects about 6 million
people.(1) With such relevant numbers of people affected and disability adjusted life years lost, CD is a poverty-related
and poverty-promoting disease.
Although data describe a relevan
...
This report outlines the coordination and partnership between two key ministries (Education and Public Health) in Kenya, other line ministries, the private sector, NGOs and the community in implementing the first phase of a sub-national school-based deworming exercise. The areas targeted included Co
...
WASH in schools during a cholera response is important due to the strong correlation between WASH and IPC. Not only can it impact the health and well-being of students and staff but also facilitate the potential spread of the disease via the congregation of children and adults from multiple househol
...
Accessed on 31.03.2023
COUNTDOWN Nigeria has applied a Participatory Action Research (PAR) approach to improve equity of Mass Administration of Medicines (MAM) and inform Neglected Tropical Disease (NTD) policy through an enhanced community engagement strategy. A situational analysis conducted i
...