Filter
7270
Text search:
social
factors
Featured
588
1855
Language
6934
207
190
132
83
63
39
28
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
6
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Document type
4216
1373
774
353
257
107
103
41
21
11
9
4
1
Countries / Regions
311
293
211
168
154
143
138
136
127
126
126
125
117
104
103
102
101
97
97
92
76
74
60
59
55
54
54
50
50
48
46
43
43
43
38
37
35
34
32
32
32
32
29
29
28
27
27
25
25
25
24
24
21
18
18
18
16
16
15
15
15
14
13
13
12
12
12
12
11
11
11
10
10
9
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
6
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
806
361
309
210
191
152
132
106
101
89
71
50
40
37
37
37
34
34
32
31
31
29
28
28
27
27
26
26
26
25
25
24
24
22
22
21
21
21
21
20
20
20
20
20
19
19
19
18
18
18
18
17
17
17
17
17
16
16
16
16
15
15
15
15
14
14
14
14
14
14
13
13
13
13
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
11
11
11
11
11
10
10
10
10
10
10
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Publication Years
1
1959
4594
683
27
4
1
1
Category
2691
439
399
375
265
159
23
7
2
1
Toolboxes
796
631
535
367
342
309
208
201
162
156
153
145
145
133
107
100
69
60
41
38
36
33
31
3
2
2
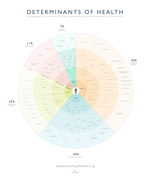
89% of health occurs outside of the clinical space through our genetics, behavior, environment and social circumstances. These factors are known as the so
...
cial determinants of health. Despite their importance, attempts to integrate the determinants into a single visualization have been limited.
Accessed 30th March 2019
more
Lancet 2021; 398: Series: Heat and Health
Hot weather and heat extremes harm human health, with poverty, ageing, and chronic illnesses as aggravating factors. As the global community contends with even hotter weather in a changing climate, there i
...
s a pressing need to better understand the most effective prevention and response measures, particularly in low-resource settings. In this two-paper series, the physiological, social, and environmental factors that contribute to individual heat vulnerability, and the megatrends affecting future heat-related morbidity and mortality at the population level, are comprehensively reviewed. Solutions to address the physiological heat strain that underlies the negative health effects of heat extremes and hot weather, which can be employed across a range of settings at individual, building, and landscape scales, are presented.
more
Women, the elderly, adolescents, youth, and children,
persons with disabilities, indigenous populations, refugees,
migrants, and minorities experience the highest degree
of socio-economic marginalization. Marginalized people
become even more vulnerable in emergencies.1 This is due
to
...
factors such as their lack of access to effective surveillance
and early-warning systems, and health services. The
COVID-19 outbreak is predicted to have significant impacts
on various sectors.
The populations most at risk are those that:
• depend heavily on the informal economy;
• occupy areas prone to shocks;
• have inadequate access to social services or political
influence;
• have limited capacities and opportunities to cope and
adapt and;
• limited or no access to technologies.
By understanding these issues, we can support the capacity
of vulnerable populations in emergencies. We can give
them priority assistance, and engage them in decision-making
processes for response, recovery, preparedness, and
risk reduction.
more
Climate change, increasing population densities, and intensified globalisation in trade, travel and migration are among the most important factors shaping the 21st century. Each impacts upon population health and the risk of infectious disease, part
...
icularly those originating at the human-animal-environmental interface. The recognition that many risk drivers of infectious disease fall outside of the typical domain of the health sector creates the challenge of identifying and pursuing priorities for cross-sectoral action aimed at strengthening global health security. In response, the One Health concept has emerged, as have related initiatives addressing Planetary Health and Biodiversity and Human Health. From a public health perspective and operationally speaking, the One Health approach offers great potential, emphasising as it does cooperation and coordination between multiple sectors. Yet despite having been a focal point for discussion for over a decade, numerous challenges facing the implementation of One Health preparedness strategies remain. While some are technical, related to the requirement for innovative early warning systems or new vaccines, for example, others are institutional and cultural in nature, given the transdisciplinary nature of the topic. There have thus been calls to address One Health from multiple perspectives, from ecology to the social sciences. In order to further explore this issue and to identify priority areas for action for strengthening One Health preparedness in Europe, ECDC convened an expert consultation on 11–12 December 2017.
more
COVID-19 Vaccines: 1 Safety Surveillance 2 Manual
While there is no indication that pregnant women have an increased susceptibility to infection with SARS-CoV-2, there is evidence that pregnancy may increase the risk of severe illness and mortality from COVID-19 disease in comparison with non-pregn
...
ant women of reproductive age. As seen with non-pregnant women, a high proportion of pregnant women have asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe disease is associated with recognized medical (e.g., high body-mass index (BMI), diabetes, pre-existing pulmonary or cardiac conditions) and social (e.g., social deprivation, ethnicity) risk factors. Pregnant women with symptomatic COVID-19 appear to have an increased risk of intensive care unit admission, mechanical ventilation and death in comparison with non-pregnant women of reproductive age, although the absolute risks remain low. COVID-19 may increase the risk of preterm birth, compared with pregnant women without COVID-19, although the evidence is inconclusive.
more
Leishmaniasis is a vector-borne disease with a wide variety of parasite species, reservoirs, and vectors involved in transmission. It is caused by different species of the protozoa Leishmania and is transmitted to animals and humans through a bite of insects in the Psychodidae family. Its presence i
...
s directly linked to poverty, but social, environmental, and climatalogic factors directly influence the disease's epidemiology.
more
Severe and difficult asthma in a low- and middle-income country (LMIC) can relate to lack of availability of basic medications; potentially reversible factors such as poor adherence or comorbidities such as obesity inhibiting a good response to trea
...
tment; and (rarely) true severe, therapy-resistant asthma. However, definitions of severity should encompass not merely doses of prescribed medication, but also underlying risk. The nature of asthmatic airway disease shows geographical variation, and LMIC asthma should not be assumed to be phenotypically the same as that in high-income countries (HICs). The first assessment step is to ensure another diagnosis is not being missed. Largely, political action is needed if children with asthma are to get access to basic medications. If a child is apparently not responding to low dose, simple medications, the next step is not to increase the dose but perform a detailed assessment of what factors (for example co-morbidities such as obesity, or social factors like poor adherence) are inhibiting a treatment response; in most cases, an underlying reason can be found. An assessment of risk of future severe asthma attacks, side-effects of medication and impaired lung development is also important. True severe, therapy-resistant asthma is rare and there are multiple underlying molecular pathologies. In HICs, steroid-resistant eosinophilia would be treated with omalizumab or mepolizumab, but the cost of these is prohibitive in LMICs, the biomarkers of successful therapy are likely only relevant to HICs. In LMICs, a raised blood eosinophil count may be due to parasites, so treating asthma based on the blood eosinophil count may not be appropriate in these settings.
more
People on the move – migrants, refugees, asylum seekers and other displaced populations – face extraordinary risks to their lives, safety, dignity, human rights and well-being.
In part this is connected to the core reasons that lead to migration and displacement, ranging from violence, persec
...
ution, conflict, poverty, political and social issues, as well as disasters and the adverse effects of climate change. In 2021, we are seeing the compounding factors of the COVID-19 pandemic and the climate crisis driving higher numbers of people to migrate, exacerbating risks and vulnerabilities.
more
It is widely understood that the food insecurity crisis in the Sahel and the Horn of Africa is one of the world’s fastest growing and most neglected crises. It lacks sufficient global focus, resources and urgency. As in so many crises, women and girls are disproportionately affected and shoulder t
...
he consequences of protracted neglect, with unconscionable impacts on their safety, life chances and agency.
Gaining a holistic view of the gendered drivers, risks and impacts of food insecurity in the Sahel and the Horn of Africa is difficult. This is due to a lack of data and prioritization, and the large geographical and socioeconomic terrain covered by both regions. However, what we do know about this crisis is more than enough to urgently address the needs of women and girls.
An OCHA discussion paper on this topic (which will be published imminently, and from which this policy brief is drawn) found that there is:
A strong risk of profound regression in gender equality gains made to date in the countries of concern, including on education, sexual and reproductive health, and the economic independence of women and girls (with knock-on effects on broader humanitarian and development outcomes).
An increasing challenge to reverse what must be recognized as a protracted and growing gender-based violence (GBV) emergency in the Sahel and the Horn of Africa.
The food insecurity crisis in the Sahel and the Horn of Africa is protracted, multidimensional and highly gendered, with spiralling impacts on gender equality and food security outcomes. It is driven by interwoven and overlapping factors, including climate change, political instability, conflict, socioeconomic conditions, migration and displacement and, more recently, COVID-19 and the war in Ukraine. Interlinked with these factors are gendered structural drivers of food insecurity, including deeply entrenched gender inequalities and harmful social norms. Gendered risks and impacts of food insecurity include alarming limitations on access to education, sexual and reproductive health rights, women’s agency and participation, and dramatic increases in different existing forms of GBV and the emergence of new ones. Recognition of such gendered dimensions of food insecurity and of the need for a multisectoral approach in the response is key to addressing the crisis, along-side sustained commitment and adequate allocation of resources. This policy brief draws out key findings from the OCHA discussion paper on this topic, which includes a desk review of studies, assessments and reports, and interviews with local women’s organizations on the front lines of the food insecurity crisis in communities across both regions.
Below are the most pressing gendered drivers, risks and impacts of food insecurity (not in order of priority), as well as key gaps in the current humanitarian response to food insecurity, and recommendations to take forward.
more
WHO and UNICEF have established recommendations for breastfeeding practices. Although every mother decides how to feed her child, this decision is strongly influenced by economic, environmental, social and political
...
factors. The Global Breastfeeding Scorecard analyzes indicators on how countries protect, promote and support breastfeeding through funding or policies.
more
Considerable energy has been expended over the last two decades in developing methods for identifying the presence of asthma among participants in population studies. The objective of this endeavour has commonly been to enable epidemiological research on risk
...
factors for asthma, with the ultimate aim of preventing the disease. However, there are other reasons for measuring the prevalence of asthma in populations, including the desire to assess the burden of disease attributable to asthma, to track changes over time, and to compare the prevalence among population groups defined by geographical, demographic or social factors. Two major international collaborative studies arising from this work have made major contributions to our knowledge about asthma
more
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aim to transform our world. They are a call to action to end poverty and inequality, protect the planet, and ensure that all people enjoy health, justice and prosperity. It is critical that no one is left behind. In 2015, all the countries in the United
...
Nations adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. It sets out 17 Goals, which include 169 targets. These wide-ranging and ambitious Goals interconnect. SDG 3 is to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. It has 13 targets measured through 26 indicators. However, a person’s health and well-being are affected not only by disease and treatment, but also by social and economic factors such as housing, poverty and education. Health targets can therefore also be found across the other SDGs. This fact sheet shows how alcohol consumption undermines commitments to achieve 13 of the 17 SDGs, impacting on a range of health-related indicators, such as child health, infectious diseases and road injuries as well as much broader range of indicators related to economic and social development, environment and equality. The inclusion of a specific target on harmful use of alcohol (SDG 3.5: strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance abuse, including narcotic drug abuse and harmful use of alcohol) into the SDGs demonstrates the key role of alcohol within the global development agenda. The factsheet highlights positive examples of Member States’ experiences. It provides a short overview of the most cost-effective and feasible policy recommendations to reduce alcohol consumption and alcohol-attributable burden in the WHO European Region, in line with the European Action Plan to Reduce the Harmful Use of Alcohol. It also suggests some important resources for Member States. This factsheet was launched as part of the European Awareness Week on Alcohol Related Harm 2020.
more
Ethnic disparities in COVID-19 persist, with increased rates of infection, severe disease, and death among people from minority ethnic groups. COVID-19 vaccination rates also remain lowest in these communities compared with white people in the UK. Among people older than 18 years, the proportion who
...
have had three COVID-19 vaccinations in England in March, 2022, was lowest among Black Caribbean (38%), Black African (45%), and Pakistani (45%) ethnic groups. These disparities are likely to be attributed to the intersection of key social determinants, including socioeconomic factors such as deprivation, overcrowding, and working patterns and conditions,
alongside discrimination and structural violence in the health-care system and society.
more
Social and behavior change (SBC) professionals have often been tasked to find ways to influence knowledge, attitudes, and practices, about vaccines. Now that the COVID-19 vaccines are becoming available worldwide, renewed emphasis and urgency for SB
...
C efforts arise.
To that end, WHO has offered three factors that play a role in vaccine hesitancy, the first two of which can be addressed by SBC: Complacency: Low perceived risk of vaccine-preventable diseases, and vaccination not deemed necessary. Other life/health issues are a greater priority.
Confidence: Low levels of trust in vaccines, in the delivery system, and in health authorities
Convenience: Barriers related to geographic accessibility, availability, affordability, and acceptability of services
This resource page provide a selection of SBC research, tools, and examples that aid in understanding this issue, especially in light of the recent availability of COVID-19 vaccines and the urgency for immunization worldwide.
more
Dengue is a mosquito-borne viral disease that has rapidly spread to all regions of WHO in recent years. Dengue virus is transmitted by female mosquitoes mainly of the species Aedes aegypti and, to a lesser extent, Ae. albopictus. These mosquitoes are also vectors of chikungunya, yellow fever and Zik
...
a viruses. Dengue is widespread throughout the tropics, with local variations in risk influenced by climate parameters as well as social and environmental factors.
more
Noncommunicable Diseases Data Portal
recommended
Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) – chief among them, cardiovascular diseases (heart disease and stroke), cancer, diabetes and chronic respiratory diseases – cause nearly three-quarters of deaths in the world. Their drivers are social, environment
...
al, commercial and genetic, and their presence is global. Every year 17 million people under the age of 70 die of NCDs, and 86% of them live in low- and middle-income countries.
Users can explore the data below by country, accessing detailed information on noncommunicable diseases and their key risk factors
more
Leishmaniasis is a vector-borne disease with a wide variety of parasite species, reservoirs, and vectors involved in transmission. It is caused by different species of the protozoa Leishmania and is transmitted to animals and humans through a bite of insects in the Psychodidae family. Its presence i
...
s directly linked to poverty, but social, environmental, and climatalogic factors directly influence the disease's epidemiology.
more
The control and elimination of schistosomiasis have over the last two decades involved several strategies, with the current strategy by the World Health Organization (WHO) focusing mainly on treatment with praziquantel during mass drug administration (MDA). However, the disease context is complex wi
...
th an interplay of social, economic, political, and cultural factors that may affect achieving the goals of the Neglected Tropical Disease (NTD) 2021-2030 Roadmap. There is a need to revisit the current top-down and reactive approach to schistosomiasis control among sub-Saharan African countries and advocate for a dynamic and diversified approach.
more
Our aim is to review current asthma epidemiology, achievements from the last 10 years, and persistent challenges of asthma man- agement and control in low-middle income countries (LMICs). Despite global efforts, asthma continues to be an important public health problem worldwide, particularly in poo
...
rly resourced settings. Several epidemiological studies in the last decades have shown significant variability in the prevalence of asthma globally, but generally a marked increase in LMICs resulting in significant mor- bidity and mortality. Poverty, air pollution, climate change, exposure to indoor allergens, urbanization and diet are some of the factors that contribute to inadequate control and poor outcomes in developing countries. Although asthma guidelines have been developed to raise awareness and improve asthma diagnosis and treatment, problems with underdiagnosis and undertreatment are still common. In addition, important social, financial, cultural and healthcare barriers are common obstacles in LMICs in achieving control. Given the high burden of asthma in these countries, adaptation and implementation of national asthma guidelines tailored to local needs should be a public health priority. Governmental commitment, education, better health system infrastructure, access to care and effective asthma medications are the cornerstone of achieving success.
more
In Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC), one maternal death was registered every hour in 2020. That same year, the trend in the maternal mortality ratio (MMR) for the Region of the Americas regressed alarmingly and unprecedentedly to the levels seen two decades ago. In addition to indicating a wors
...
ening of health outcomes, these figures also signal a deepening of inequalities, representing thousands of individual, unacceptable tragedies that in most cases could have been preventable. Maternal death is the result of a multifactorial process in which structural elements such as the economic system, environmental conditions, and culture interact. Other factors related to social inequality are also present, such as racism, poverty, gender inequality, and lack of access to the education system. The current situation calls for urgent mobilization of the health systems of LAC countries in order to strengthen efforts to combat maternal mortality, especially in countries that are still far from achieving the SHAA2030 regional target. For this reason, a preventive, health-promoting, life-course-based approach is needed, with models of care centered on women, families, and the community Scientific evidence shows that health systems with a solid foundation in primary health care (PHC) achieve better outcomes, greater equity, and reduced health expenditures. To address this, PAHO proposes a strategy, aimed primarily at women who are in the most vulnerable situation, who are the ones who represent the greatest burden of maternal mortality, to accelerate the reduction of maternal mortality in the Region of the Americas, based on the expansion and strengthening of PHC.
more