Filter
286
Text search:
foodborne
diseases
Featured
24
54
Language
Document type
91
79
40
29
16
12
6
5
4
3
1
Countries / Regions
20
9
7
5
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
56
27
26
14
8
7
7
Toolboxes
57
52
29
18
17
9
8
8
6
6
6
4
4
3
2
1
1
1
As the number of transboundary pest and animal and foodborne disease outbreaks rises, so does the number of people who are chronically hungry due to these and other factors. The correlation can be explained by the link between our health and that of
...
Website last accessed on 14.04.2023
Food-borne trematode infections are zoonotic, and their pathogens can be transmitted to humans only after the completion of a complex life cycle, some stages of which take place in the body of an intermediate animal host. The first intermediate hosts of all tr
...
Notable progress has also been made on other key health indicators such as reducing maternal, infant and child deaths and malnutrition, increasing immunization coverage, eliminating infectious diseases such as polio and reducing the incidence of mal
...
The most frequent health problems of newly arrived refugees and migrants include accidental injuries, hypothermia, burns, gastrointestinal illnesses, cardiovascular events, pregnancy- and delivery-related complications, diabetes and hypertension. Female refugees and migrants frequently face specific
...
WASH Training for Hygiene Promotion Staff.
This manual has been designed to train NRC hygiene promotion incentive staff on ... concept and importance of hygiene, diseases that are present or a risk in Kakuma Refugee. Camp and how to prevent them; m
...
Fascioliasis is caused by two species of parasitic flatworms or trematodes that mainly affect the liver. It belongs to the group of foodborne trematode infections and is a zoonosis, meaning an animal infection that may be transmitted to humans.
WHO promotes the inclusion of foodborne trematodiases among the targets of preventive chemotherapy interventions. With the aim of providing access to quality medicines, WHO has negotiated with Novartis Pharma AG whereby Novartis donates triclabendaz
...
Foodborne trematodiases are caused by parasitic trematode worms. People become infected by eating raw or undercooked fish, crustaceans and vegetables that contain the larval worms.
The internationally recognized criteria for diagnosis of neurocysticercosis include a requirement for neuroimaging techniques, such as computerized tomography (CT) and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ideally supported by serology. These facilities are not available in all settings, especially i
...
2nd edition
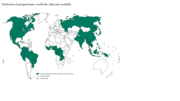
Map of Distribution of Paragonimiasis, worldwide latest year available.
Foodborne trematodes are a group of diseases that include the parasites Clonorchis, Opisthorchis, Fasciola and Paragonimus. T
...
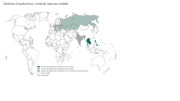
Map of Distribution of opisthorchiasis, worldwide, latest year available.
Foodborne trematodes are a group of diseases that include the parasites Clonorchis, Opisthorchis, Fasciola and Paragonimus
...
Website last accessed on 14.04.2023
Food-borne trematode infections are zoonotic, and their pathogens can be transmitted to humans only after the completion of a complex life cycle, some stages of which take place in the body of an intermediate animal host. The first intermediate hosts of all tr
...
Weekly epidemiological record Relevé épidémiologique hebdomadaire 27 MARCH 2015, 90th YEAR / 27 MARS 2015, 90e ANNÉE No. 13, 2015, 90, 121–132
GUIDE PRATIQUE À L’INTENTION DES PROGRAMMES DE LUTTE CONTRE LES MALADIES TROPICALES NÉGLIGÉES
This toolkit provides step-by-step guidance to NTD programme managers and partners on how to engage and work collaboratively with the WASH community to improve delivery of water, sanitation and hygien
...
Traditional food markets play important economic, cultural, and social role and are sources of livelihood for millions of people in urban and rural areas. The manual Five keys for safer traditional food markets: risk mitigation in traditional food markets in the Asia-Pacific Region aims to support a
...
Zoonotic tuberculosis (TB) is a form of TB in people predominantly caused by the bacterial species, Mycobacterium bovis, which belongs to the M. tuberculosis complex. The implications of zoonotic TB go beyond human health. The organism is host-adapted to cattle, where it is refer
...
Current evidence that the climate is changing is overwhelming. Impacts of climate change and variability are being observed: more intense heat-waves, fires and floods; and increased prevalence of food- water- and vector-borne diseases. Climate chang
...
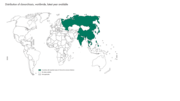
Map of Distribution of clonorchiasis, worldwide.
Foodborne trematodes are a group of diseases that include the parasites Clonorchis, Opisthorchis, Fasciola and Paragonimus. These parasitic flukes
...