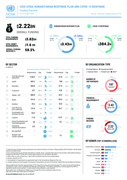
Filter
1996
Text search:
donor
funding
Featured
Recommendations
130
New Publications
674
Language
English
1968
French
30
Spanish
22
Arabic
16
Russian
14
Portuguese
10
Chinese
8
German
4
Nepali
4
Indonesian
4
Swahili
2
Bengali
2
Urdu
2
Turkish
2
Serbian
2
Vietnamese
2
Croatian
2
Bosnian
2
Japanese
2
Dari
2
Pashto
2
Burmese
2
Khmer
1
Malay
1
Korean
1
Ukrainian
1
Sinhalese
1
Document type
No document type
1323
Studies & Reports
354
Guidelines
102
Strategic & Response Plan
95
Manuals
68
Situation Updates
18
Fact sheets
15
Training Material
10
Infographics
5
Resource Platforms
4
Brochures
1
Online Courses
1
Countries / Regions
Global
116
Liberia
65
Kenya
60
Sierra Leone
59
Nigeria
58
Ethiopia
57
Uganda
57
Malawi
54
Myanmar / Burma
51
Zambia
48
Rwanda
45
Nepal
44
Syria
42
Tanzania
31
Ghana
28
Bangladesh
28
Namibia
28
Africa
28
India
27
South Sudan
27
Congo, Democratic Republic of
26
Cambodia
26
Ukraine
26
Lesotho
22
Guinea
20
Zimbabwe
19
South Africa
19
Haiti
18
Mozambique
18
Western and Central Europe
17
Asia
17
Philippines
16
Botswana
15
Afghanistan
13
Latin America and the Carribbean
13
Pakistan
12
Senegal
11
Central African Republic
11
Eastern Europe
11
Indonesia
9
Yemen
9
East and Southern Africa
9
South–East Asia Region
9
Venezuela
9
Burkina Faso
7
Mali
7
West and Central Africa
7
Laos
7
China
6
Benin
6
Colombia
6
Middle East and North Africa
6
Côte d’Ivoire / Ivory Coast
5
Somalia
5
Jordan
5
Sudan
5
Cameroon
4
Lebanon
4
Eswatini/ Swaziland
4
Albania
4
Russia
4
Georgia
4
Vietnam
4
Thailand
3
Serbia
3
Tajikistan
3
Japan
3
Guinea-Bissau
2
Germany
2
Gambia
2
Papua New Guinea
2
Peru
2
Brazil
2
North Macedonia
2
Croatia
2
Sri Lanka
2
Palestine
2
Armenia
2
Moldova
2
Kyrgyzstan
2
Jamaica
2
Niger
1
Togo
1
Iraq
1
Turkey
1
Egypt
1
Chad
1
Malaysia
1
El Salvador
1
Libya
1
Angola
1
Madagascar
1
Western Pacific Region
1
Eastern Europe and Central Asia
1
Other region
1
Fiji
1
Southern Africa
1
Timor Leste/ East Timor
1
Iran
1
Turkmenistan
1
Portugal
1
Spain
1
Azerbaijan
1
Bosnia and Herzegovina
1
Authors & Publishers
World Health Organization WHO
146
World Health Organization
84
et al.
82
World Health Organization (WHO)
74
UNAIDS
69
World Health Organisation (WHO)
49
USAID
43
UNICEF
39
WHO
25
Federal Ministry of Health, Nigeria
14
Human Rights Watch
14
Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs OCHA
14
Oxfam
14
Save the Children
14
PEPFAR
13
Stop TB Partnership
13
UNFPA
13
Ministry of Health and Social Services (MOHSS)
12
World Health Organization (Europe)
12
International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies
11
Ministry of Health, Zambia
11
The Global Fund
11
UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs
11
ICF International
10
PLOS One
10
UNDP
10
World Bank
10
Ministry of Health
9
Ministry of Health, Malawi
9
The World Bank
9
UN Children's Fund UNICEF
9
AidData at William & Mary
8
BMJ Global Health
8
Ministry of Health, Ghana
8
National Agency for the Control of AIDS (NACA)
8
Government of Sierra Leone, Ministry of Health and Sanitation
7
Ministry of Health and Social Welfare, Tanzania
7
Ministry of Health, Republic of Uganda
7
UN High Commissioner for Refugees
7
UN High Commissioner for Refugees UNHCR
7
UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA)
7
United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF)
7
World Health Organization Europe
7
ALNAP
6
Christoffel Blinden Mission (CBM)
6
Government of Malawi, Ministry of Health
6
Ministry of Health, Kenya
6
Ministry of Health, Rwanda
6
The Republic of the Union of Myanmar, Ministry of Health and Sports
6
UNAIDS (Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS)
6
Asian Disaster Preparedness Center, Tsunami Global Lessons Learned Project
5
Center for Excellence in Disaster Management and Humanitarian Assistance
5
Department of Health (DOH)
5
Eurasian Harm Reduction Network
5
European Interagency Security Forum (EISF)
5
Health Policy and Planning
5
Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME)
5
International Federation of Red Cross And Red Crescent Societies IFRC
5
Médecins sans Frontières
5
Ministry of Health and Social Welfare, Liberia
5
Ministry of Health Uganda
5
Ministry of Health, Uganda
5
National AIDS
5
Pan American Health Organisation PAHO
5
United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
5
United States Agency for International Development
5
Avert
4
Human Resources for Health
4
Inter-Agency Standing Committee IASC
4
International HIV/AIDS Alliance
4
International Rescue Committee
4
Management Sciences for Health
4
MEASURE DHS
4
Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF)
4
Ministry of Health, Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia
4
OCHA
4
Protection Cluster
4
Republic of Kenya, Ministry of Health
4
Results for Development (R4D)
4
The Lancet
4
UNITAID
4
World Health Organization WHO, Regional Office for Europe
4
World Health Organization WHO, Regional Office for Africa
4
ACT Alliance
3
Africa Center for Disease Control and Prevention
3
C. Hamelmann
3
CDC
3
END TB
3
EngenderHealth
3
EU
3
European Commission
3
Family Planning 2020
3
Federal Ministry of Health, Ethiopia
3
Federal Ministry of Health, Uganda
3
Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery
3
Government of Liberia
3
Government of Malawi
3
Government of Nepal Ministry of Health and Population, National Centre for AIDS and STD Control
3
Government of Uganda
3
Health Research Policy and Systems
3
IFRC
3
IFRC - International Federation of Red Cross
3
Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation
3
International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC)
3
International Labour Organization
3
Joint United Nations Programme on HIV
3
Ministry of Health & Social Welfare, Liberia
3
Ministry of Health and Social Welfare Liberia
3
Ministry of Health and Social Welfare, National AIDS Control Programme, Tanzania
3
Ministry of Health Ghana
3
Ministry of Health, Liberia
3
National Agency for the Control of AIDS (NACA), Abuja Nigeria
3
National HIV
3
OECD
3
Patel P.
3
Plan International
3
PLoS Med
3
PLOS Medicine
3
Regional Network for Equity in Health in east and southern Africa (EQUINET)
3
Regional Office for Africa
3
Rüppel T.
3
The Global Fund To fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria
3
UN Development Programme
3
UNAIDS (Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS)
3
United Nations Division for Social Policy Development (DSPD) & United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA)
3
United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA)
3
UNOPS
3
World Bank Group
3
World Food Programme
3
World Food Programme (WFP)
3
World Health Organization (WHO), Regional Office for South-East-Asia
3
World Health Organization WHO, Regional Office for Africa
3
World Health Organization, Regional Office for Africa
3
World Vision
3
A. Kamarulzaman
2
A. Sönnerborg
2
Aagaard-Hansen, J.
2
Action Against Hunger
2
Africa CDC
2
Africa CDC Centres for Disease Control and Prevention
2
African Union
2
AIDS Free (Strenghtening High Impact Interventions for a AIDS-free Generation)
2
Amnesty International
2
Assessement Capacities Projekt
2
Atun, R.
2
B. Pick
2
Barrett, O.L.
2
Birkman, L.
2
BMC Public Health
2
Brock, S.
2
Brot für die Welt
2
Brunner B., J. Barnes, A. Carmona et. al.
2
Bull World Health Organ
2
C. Beyrer
2
C. Daniels, et al.
2
care
2
Catholic Relief Services
2
CBM
2
CCM Georgia
2
Center for Global Development
2
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
2
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC
2
Centre for Health & Infectious Disease Research
2
Channel Research
2
Child Protection in Crisis
2
Christoffel-Blindenmission (CBM)
2
Constella Futures
2
D. Raben
2
D. Wolfe
2
E. Aaraj
2
E. Subata
2
ECHO
2
Elsevier
2
European Union
2
Federal Ministry of Health Nigeria
2
Federal Ministry of Health of Ethiopia
2
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)
2
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations FAO
2
G. Shaw
2
German Bishops' Conference Research Group on International Church Affairs
2
Ghana Health Service
2
Global Financing Facility (GFF)
2
Global Health Action
2
Global Network of People Living with HIV (GNP+)
2
Global Polio Eradication Initiative
2
Globalization and Health
2
Government of Nepal
2
Government of Tanzania
2
Government of Zambia
2
Grollman, C.
2
H. Getahun
2
H. Ingold
2
H. Sakamoto
2
Handicap International
2
Health Affairs
2
Health Policy Project
2
Health System Trust HST
2
Human Rights Watch HRW
2
IASC Inter-Agency Standing Committee
2
ICASO
2
ICF
2
ICF Macro
2
Indian Council of Medical Research
2
Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
2
Inter-Agency Network for Education in Emergencies
2
Inter-Agency Network for Education in Emergencies (INEE)
2
Inter-agency Task Force on Financing for Development
2
International Coalition for Trachoma Control ICTC
2
International Military Council on Climate and Security
2
International Oranization for Migration
2
International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease
2
IPPF, UNFPA, WHO, UNAIDS
2
Irish Aid
2
Jens Martens and Karolin Seitz
2
Journal of the International AIDS Society
2
JSI Research & Training Institute
2
Kamala Achu, Kathy Al Jubah, Svein Brodtkorb, et al.
2
Karolin Seitz
2
Kenya Ministry of Health
2
KNCV TUBERCULOSIS FOUNDATION
2
Lancet
2
Lesotho National Federation of Organisations of the Disabled (LNFOD)
2
LIGHT FOR THE WORLD
2
M. K. Sugai et al.
2
M. Mansfeld
2
M. Smelyanskaya, J. Duncan (The Focus Group Consulting)
2
Maitland, K.
2
Manuel Sanchez-Montero and Núria Salse Ubach
2
McGahey, Christopher
2
MCHIP
2
Measurement, Learning & Evaluation of the Kenya Urban Reproductive Health Initiative (Tupange), et al.
2
Ministry of Health & Ministry of Local Government, Gabarone, Botswana
2
Ministry of Health and Sanitation, Sierra Leone
2
Ministry of Health and Social Welfare (MoHSS), Kingdom of Lesotho
2
Ministry of Health, Cambodia
2
Ministry of Health, Ethiopia
2
Ministry of Health, Kingdom of Lesotho
2
Ministry of Health, Republic of Botswana
2
Myanmar Red Cross Society
2
National Health Insurance Scheme
2
National Institute of Statistics of Rwanda (NISR), the African Institute for Development Policy (AFIDEP) and UNFPA
2
Nomura, S.
2
Norwegian Refugee Council
2
Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA)
2
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
2
Overseas Development Institute
2
Pan American Health Organization
2
PLOS Medecine
2
POZ
2
President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR)
2
PRESIDENT’S MALARIA INITIATIVE
2
Pubmed
2
Reliefweb
2
Reliefweb OCHA Services
2
Report the Abuse
2
Research Gate
2
Rüppel J.
2
Rwanda Biomedical Center - Institute of HIV
2
Sanders, S.
2
Schäferhoff, M.
2
SCMS
2
SINTEF Health Research
2
South African National AIDS Council
2
Terre des hommes
2
The DHS Program ICF
2
The High-Level Panel on International Financial Accountability, Transparency and Integrity for Achieving the 2030 Agenda (FACTI Panel)
2
The International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies IFRC
2
The Sphere Project
2
The United States President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR)
2
Three Millennium Development Goal Fund (3MDG)
2
Treatment Action Group
2
U.S. President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief
2
Uganda AIDS Commission
2
UN Industrial Development Organization
2
UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, Regional Interagency Standing Committee, Southern Africa
2
UN Women
2
UNAIDS (Joint United Nations Programme on HIV
2
UNCT Zambia
2
UNHCR
2
Unitaid (Innovation in Global Health)
2
UNITAID Secretariat, World Health Organization
2
United Nations
2
United Nations (UN)
2
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
2
United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNISDR)
2
UNODC
2
USAID (From the American People)
2
USAID, et al.
2
USAID, Health Systems 20
2
War Child Holland
2
War Trauma Foundation
2
Watts, S.
2
World Food Program WFP
2
World Food Programme WFP
2
World Health Organisation
2
World Health Organization WHO
2
World Health Organization ( WHO), Regional Office for South-East-Asia
2
World Health Organization (Regional Office for South-East-Asia)
2
World Health Organization WHO, Regional Office of Africa
2
World Health Organization WHO, Regional Office of Europe
2
World Health Organization WHO, UNICEF
2
World Health Organization, Europe
2
World Health Organization. Regional Office for South-East Asia
2
World Heart Federation
2
2021 Malawi Sustainability Index and Dashboard Summary
1
3 Good Health and well-beeing
1
390: 898&ndash
1
3RP
1
912
1
[Republic of Libera, Ministry for Health]
1
A. Alebel
1
A. Armstrong
1
A. Baddeley
1
A. Bokazhanova
1
A. Bolotbaeva
1
A. Boltaev
1
A. Chu, Z. Li et al.
1
A. E. Kendall
1
A. Fuchs
1
A. G. Yemaneberhan
1
A. Gebrie
1
A. Gheorghe
1
A. Gupta
1
A. H. Sohn
1
A. Horban
1
A. Hovhannesyan, P. Moonan, A. Dadu
1
A. J. Shattock
1
A. Judd
1
A. Kanchar
1
A. Miruka
1
A. Murray-Zmijewski
1
A. Pantoja et al.
1
A. Sharma
1
A. T. Makadzange
1
A. Tandon et al.
1
A. Teltschik
1
A. Tokar
1
A. Wirtz
1
A.B. Ghartey
1
A.I. Kryvoruk
1
A.V. Sudakova
1
Aantjes, C.
1
Aaron M Kipp, Margaret Maimbolwa, Marie A Brault et al.
1
Abubakar, I.
1
Academic Journals
1
Academy for Educational Development
1
Acclimatise, Climate and Development Knowledge Network (CDKN)
1
ACF International Network
1
ACF International Network and the Oakland Institute
1
ACF International Network and Tripode
1
Achary A.
1
ACTafrica, HNP
1
Action Contre la Faim (ACF)
1
Action contre la Faim France
1
ACTION global health advocacy partnership
1
ACTION partner oranizations
1
ActionAid Myanmar
1
Adams, J.
1
ADCAP Age an& Disability Capactiy
1
Adele Harmer and Abby Stoddard, Humanitarian Outcomes
1
Adelekan, B.
1
Advance Family Planning (AFP)
1
Advancing Partners & Communities (APC)
1
Advantage Africa, FIRAH, Resource Center Applied Research and Disability
1
AfClix
1
Afghanistan Reconstruction Trust Fund (ARTF)
1
African Centre for the Constructive Resolution of Disputes
1
African Development Bank
1
African Development Bank Group
1
African Development Fund
1
African Evaluation Journal
1
African Palliative Care Association
1
African Programme for Onchocerciasis Control APOC
1
African Religious Health Assets Programme (ARHAP)
1
African Union (AU)
1
Aga Khan Health Services, Kenya
1
Ager, A, Ager, W, Stavrou, V. & Boothby, N.
1
Agni, Kathy
1
Agriculture for Impact-Imperial College of London
1
AHVP
1
AIDS and Rights Alliance for Southern Africa
1
Aidsfonds
1
AIDSFree
1
AIDSinfo
1
Aidspan
1
akkon Hochschule für Humanwissenschaften
1
Aksoy, S.
1
Aktionsbündnis gegen AIDS
1
Al Delaimy W., Ramanathan V., Sanchez Sorondo M. et al.
1
Albanian Center for Population and Development (ACPD)
1
Alexander Butchart, David Brown, Andrew Wilson, and Christopher Mikton
1
Aliku, T. et al.
1
Alimonte, Mary D'
1
Allers, Claudia, Timothy O’Hearn, and Meba Kagone
1
Alliance for Health Policy and Systems Research
1
Alliance for Health Policy and Systems Research (AHPSR) and World Health Organization
1
Almeida C
1
ALNAP, Provention Consortium
1
Amaya M Gillespie, Rafael Obregon, Rania El Asawi, et al.
1
American Academy of Paediatrics
1
Amnesty International Publications
1
Ana Beatriz Monteiro Costa, Mario Gyoeri and Fábio Veras Soares
1
and C.J. Arnson
1
and F. Serhan
1
and L. Reilly
1
and S.J. Mason
1
Andy Barraclough
1
Andy Featherstone
1
Angwenyi, V.
1
Anna Marriott
1
Annelies Heijmans
1
ANNIEWILKINSON ANDMELISSA LEACH
1
Anthony W. Solomon, Marcia Zondervan, Hannah Kuper, et al.
1
AOSIS
1
Arias, Daniel
1
Arlington, VA: Management Sciences for Health
1
Arlington, VA: USAID’s AIDS Support and Technical Assistance Resources, AIDSTAR-One, Task Order 1
1
Armenian National AIDS Center
1
Armenian Red Cross Disaster Management Programme
1
Armstrong, J.
1
Arne H Eide & ME Loeb
1
Arregoces L. et al.
1
Asia Pacific Observatory on Health Systems and Policies
1
Asian-Pacific Resource and Research Centre for Women (ARROW)
1
Assessment Capacities Project ACAPS
1
Atun R.
1
Australian Aid & CBM
1
Australian Government AusAID
1
AVAC (Global Advocacy for HIV Prevention)
1
Ayala, George
1
B. Akkazieva
1
B. Chimukangara
1
B. Herstad
1
B. Konstantinov
1
B. Lee, E. Pearce, D. Buscher
1
B. Noubary
1
B. O’Donnell
1
B. Parks et al.
1
B. Russell et al.
1
B. Subha Sri
1
B. Tesfaye
1
B. Weil
1
Baas, Stephan
1
Back Pack Health Worker Team (BPHWT)
1
BAff
1
Baghdadi-Sabeti , G.
1
Balaji, V., P. Rupali, K. Walia, et al.
1
Banda, P
1
Banks, L.M. & Keogh, M.
1
Baral, P.
1
BardenO'Fallon J, Barry MA, Brodish P, et al.
1
BASICS
1
Bastable, Andy and Russell, Lucy
1
Bawi, Salai Vanni
1
Beard, R. Suzanne
1
Beardsley, Kip., A. Zapfel, and T. Williamson
1
Becher, H.
1
Bendavid E. et al.
1
Benjamin O Alli [et al.]
1
Berman, D.
1
Bernard van Leer Foundation
1
Betts, A.
1
Béatrice Boyer
1
Bhutta, Zulfiqar et al.
1
Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
1
Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, et al.
1
Bioforce Development Institute – Burkina Faso Country Survey
1
Birkeland,N.M.
1
Bischöfliches Hilfswerk MISEREOR, Brot für die Welt, Global Policy Forum
1
BJOG An International Journal of Obstetics and Gynaecology
1
BMC
1
BMC Public Health (BioMed Central)
1
Bonino, F. with Jean, I. and P. Knox Clarke
1
Bonsu FA, Hanson-Nortey NN, Afutu FK et al.
1
Borghi, J. et al.
1
Bosnia and Herzegovina Council of Ministers,
1
Bouley, T. A.
1
Boyce, M.
1
BRACED Myanmar Alliance
1
Brindley, P. et al.
1
British Medical Journal (BMJ)
1
Brown S.
1
Brown, T.
1
Brunn, B.
1
Bruno Martorano, Laura Metzger, Marco Sanfilippo
1
Bruun, B.
1
Bryant Lee, Rosemary Silaa, Catherine Barker, et al.
1
Buckley, P.
1
BUKO Pharma-Kampagne
1
Bundesamt für Migration und Flüchtlinge (BAMF)
1
Burt Perrin
1
By the Committee on Ethical Aspects of Human Reproduction and Women's Health, International Federation of Gynaecologists and Obstetricians (FIGO)
1
C.
1
C. Benedikt
1
C. Clift
1
C. Fitzpatrick
1
C. Grollman
1
C. Hanlon, A. Alem, C. Lund, et al.
1
C. L. Moyes et al.
1
C. Lienhardt
1
C. Opreab
1
C. Pérez Casas
1
C. Rooney
1
C. Venkatraman
1
CAFOD
1
Cambodia, Ministry of Health, PMNCH, WHO, World Bank, AHPSR et al.
1
Campos, A.
1
CARE Evaluations
1
Care, et al.
1
CARE, International Rescue Committee, Save the Children, Women's Refugee Commission
1
Carla Silva-Matos
1
Cashin, Jennifer
1
Cassola, A.
1
Catholic Agency for Overseas Development CAFOD
1
Catholic Relief Services, CARE, Action Contre la Faim, et al.
1
Catriona Waddington, Abebe Alebachew and Jarl Chabot
1
CBM & Basic Needs UK in Uganda (BNUU)
1
CBR Africa Network, Handicap International
1
CBR Asia-Pacific Network
1
CDC et al.
1
cedpa (The Centre for Development and Population Activities)
1
Center for Innovation and Impact (CII), USAID
1
Center for Operational Analysis and Research COAR
1
Center for Pubic Health and Human Rights
1
CENTRAL MONITORING A ND EVALUATION DIVISI ON (CMED)
1
Central Statistical Agency [Ethiopia] and ICF International
1
Central Statistical Office Lusaka
1
Central TB Divison, Ministry of Health and Social Welfare, Government of India
1
Centre for Eye Research Australia
1
Centre for Heath & Infectious Disease Research
1
Centre for Maternal and Newborn Health (CMNH), from the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine (LSTM)
1
Cercone, James
1
Chagas Coalition
1
Chaitkin, Michael
1
Chama-Chiliba, C.
1
Chandani, Y.
1
Chang, Judy et al.
1
Chansa, C.
1
Chapeyama, Oliver
1
Charité
1
Charles Lwanga-Ntale
1
Charlotte Feldman-Jacobs, et al.
1
Charlson, F.J.
1
Checchi F.
1
Child Health Division, Family Health Division, Ministry of Health, Save the Children Nepal
1
Child Soldiers International
1
Children & AIDS
1
Chimimba, F.
1
Chou P.
1
Christensen, Alice et al.
1
Christina Angela Ntulo
1
Christina Wille and Larissa Fast
1
Christopher J.L. Murray1 & Julio Frenk
1
Christoplos, I. and Dillon, N. with Bonino, F.
1
Civil Society 20 (C20) - Saudi Arabia 2020
1
Clift, Jack
1
COC Netherlands
1
COC Netherlands and Columbia University – ICAP (South Africa)
1
Cohen, A., Eaton, J., Radtke, B., et al.
1
Coignez, V., Hajjou, M., and Smine
1
Colin Robson & Peter Evans
1
Collins, T.E.
1
Congressional Research Service
1
Cook, R.
1
Cordaid
1
CORE Group
1
CORE Group Nutrition Working Group, Food and Nutrition Technical Assistance III Project (FANTA), and Save the Children
1
Cornell University
1
Corporate Evaluation and Methods Operations Evaluation Department
1
Corrado Barbui, Tarun Dua, Kavitha Kolappa et al.
1
Cosgrave, J.
1
Couldrey, M.
1
Coupland R, Loye D
1
Crawford E., Suvedi M.
1
CSI
1
Cunningham, A.
1
CURATIO International Foundation
1
Currion, P.
1
Cynthia Green
1
D. B. Evans
1
D. Barr
1
D. Burrows
1
D. Cohen
1
D. Duclos et al.
1
D. Gamboa et al.
1
D. Gokengina,
1
D. Jamieson
1
D. Kerrigan
1
D. Low-Beer
1
D. Lowe, D. Hales
1
D. Mueller et al.
1
D. Ruiz
1
D. Stewart
1
D. van der Veur
1
DAC Network on Conflict, Peace and Development Co-operation and DAC Network on Development Evaluation
1
Dahab M.
1
Daniel McLaughlin
1
David Beran
1
David H. Peters, Nhan T. Tran, Taghreed Adam
1
David Marsh, Ashley Aakesson, Kechi Anah et al.
1
Davis, Bill
1
Davis, Ian
1
Davis, J.
1
De Beni, Davide
1
De La Salle Unviersity, Manila
1
de Vries D, Blair G, Morgan K
1
Deconinck H., S. Diene, P. Bahwere
1
Dedford, C.
1
Deliver Project
1
Department for International Development DFID
1
Department for International Development, Uganda
1
Department of Education, Republic of South Africa
1
Department of Global Health
1
Department of Planning and Health Information, Ministry of Health Cambodia
1
Department: Social Department Republic of South Africa
1
Dept. of Education, Nepal
1
Dermot Maher
1
Deutsche Gesellschaft für International Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
1
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH
1
Deutsche Zusammenarbeit
1
Development Initiatives
1
Development Initiatives Poverty Research Ltd.
1
Development Studies Network
1
Dey de Pryck, Jenny et al.
1
DFID
1
DHS
1
Diego J. Rodriguez, Matthijs Schuring, Nansia Constantinou et al.
1
Dingle, A.
1
Disability, CBR & Inclusive Development Journal (DCIDJ)
1
DNDi - Drugs for neglected diseases initiative
1
Doeffinger, T.
1
Dolan CB, Saunders M, BenYishay A
1
Dominique Morel, and Clara Hagens
1
Donald Dickerson and Aliyu Aminu Ahmed
1
Donaldson, Liam
1
Doug Reeler, Akke Schuurmans, Jeroen Overweel
1
Dr F Siyoi, Dr C Forshaw, Dr J Mbuva ,Dr M Thuo, Dr N Mucheru, Dr E Ominde-Ogaja, Dr R Mbindyo, Mrs R Kirika
1
Dr M.Funk
1
Dr. M. Dara
1
Dr. P. Zeitz
1
Dr. S. Godinjak
1
Dr. Z. Cardaklija
1
Dreher, A.
1
Drug Safety
1
Dumble, Sam
1
Dzabala, N. et al.
1
D’A. Richardson
1
D’Arcy Richardson, PATH, and Greg Pirio, Empower Communications
1
e National Institute of Statistics of Rwanda (NISR), the African Institute for Development Policy (AFIDEP) and UNFPA
1
E. Corbett
1
E. Goldson, Z. Abubakar et al.
1
E. Masaki
1
E. Restoy
1
E. Ross
1
E.Bernard
1
Eastern Mediterranean Region
1
ec al.
1
Economic Empowerment Section of UN Women
1
Economist Impact
1
Edwards, Jon
1
ehra (eurasian harm reduction association)
1
Eiling, E., Mulder, A. & Blommestein, N.
1
Ejembi, Clara Ladi, Tukur Dahiru, and Alhaji A. Aliyu
1
Elizabeth Lamond, and Jesee Kinyanjui
1
ELRHA
1
Emergency Capacity Building Project
1
Emergency Nutrition Network ENN
1
Emergency Operations and Emergency Response Team
1
Emily Keane, Andrea King, Anthony Awira et al.
1
Environmentally Sustainable Development supported by World Bank
1
Eric Maskin, Célestin Monga, Josselin Thuilliez and others
1
Erik Blas, Johannes Sommerfeld and Anand Sivasankara Kurup
1
Erskine D.
1
et al,
1
eta al.
1
etc al.
1
Ethiopia Central Statistical Agency and ICF International
1
Ethiopia, Ministry of Health
1
European Commission Humanitarian Aid
1
European Commission Humanitarian Aid department
1
European Commission, Humanitarian Aid
1
European Union (EU)
1
European Union EU
1
European University Institute
1
Eva-Svoboda
1
Evert, J.
1
Every Woman Every Child
1
Evidence to Action
1
F. Bozzani et al.
1
F. Brigden
1
F. Federspiel
1
F. Hariga
1
F. Kiweewa, A.Dasgupta
1
F. L. Cavallaro
1
F. Ndugulile
1
F. O. Fasina, Fasanmi O.G., Makonnen Y. J., et al.
1
F. Samuels
1
F. Terris-Prestholt
1
Family Health International (FHI)
1
Fan V.
1
Fanjul, G.
1
Farina A.
1
Fast, Larissa and Adele Waugaman
1
Fayolle, Virginie
1
Featherstone, A.
1
Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Ministry of Health
1
Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, Ministry of Health
1
Federal HIV
1
Federal Ministries of Agriculture, Environment and Health
1
Federal Ministry of Economic Cooperation and Development BMZ
1
Federal Ministry of Health (FMOH), National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS) and the National Primary Health Care Development Agency (NPHCDA)
1
Federal Ministry of Health - Nigeria Centre for Disease Control
1
Federal Ministry of Health Nigeria , World Health Organisation (WHO)
1
Federal Ministry of Health Nigeria , World Health Organisation (WHO), DFID, et al.
1
Federal Republic of Nigeria
1
Feed the Future
1
Feinstein International Center
1
Feinstein International Center, Tufts University
1
Ferguson, S.
1
Fewer S.
1
Field Actions Science Reports
1
FIGO
1
Fiji Pharmaceutical Service
1
Finucane, C.
1
Fistulacare, USAID
1
Flavia Bustreo, Marie-Paule Kieny, Lale Say et al.
1
Flavia Bustreo, Shyama Kuruvilla, Marleen Temmerman et al
1
Fleischer, K. et al.
1
Fleischer, K., et al.
1
Fleisher, Lisa
1
Flory A. et al.
1
Floyd, K.
1
Flying Publisher, Boehringer Ingelheim
1
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations FAO and African Union AU
1
Food and Nutrition Technical Assistance II Project (FANTA-2)
1
FoodSTART+
1
Forsberg, B.
1
François Grünewald
1
Frederic Mousseau
1
Fredrick K. Sawe
1
Freel
1
Freeman, M.C.
1
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine
1
Fuchs, A. and Öhler, H.
1
G. Ayala
1
G. J. Montalto
1
G. Jonboboeva
1
G. McCord
1
G. Ooms
1
G. Pirio
1
G. Sander
1
G.L. Forselv, V. Vogel, et al.
1
G7
1
Galarraga, O.
1
Gallo-Bernal, S.
1
Gamez, Laura et al.
1
Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance
1
GBI
1
Gebreselassie, Tesfayi, and Pav Govindasamy
1
Geneva Global Health Hub
1
Geofrey Odongkara, Cecilia Kihara, Jane Johnson, Hester Phillips
1
German Cooperation
1
German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ)
1
Gething, PW.
1
GFDRR
1
GFDRR Habitat for Humanity IFRC
1
Ghana AIDS Commission
1
Ghana Health Service (GHS)
1
Ghana Statistical Service
1
Ghana Statistical Service Ghana Health Service Accra, Ghana
1
Ghana, Ministry of Health
1
GHS/NMCP/JHPIEGO/MSH/GLOBAL FUND (GFATM)
1
Gilbert, B.J.
1
GIZ
1
Global Advocacy for HIV Prevention (AVAC)
1
Global AIDS Alliance
1
Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunisation (Gavi)
1
Global Burden of Disease Health Financing Collaborator Network
1
Global Forum on MSM & HIV
1
Global Fund
1
Global Fund Advocates Network
1
Global Fund, World Bank Group, Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance et al.
1
Global Green Growth Institute - GGGI
1
Global Health Watch
1
Global Health: Science and Practice
1
Global Heart
1
Global Humanitarian Assistance
1
Global Laboratory Initiative (GLI), Stop TB Partnership
1
Global Mental Health
1
Global mental health (Atilola, O.)
1
Global mental health, Cambridge University Press
1
Global Nutrition Report Stakeholder Group
1
Global Policy Forum Europe e.V.
1
Global Polio Eradication Initiative GPEI
1
Global Preparedness Monitoring Board
1
Global Protection Cluster
1
Global Protection Cluster, GPV Prevention and Response
1
Global Task Force On Cholera Control (GTFCC)
1
GOAL
1
Governance and Social Development Resource Centre HEART
1
Government of Ethiopia
1
Government of Ethiopia, UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs
1
Government of India, Central Tuberculosis Division, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
1
Government of Indonesia
1
Government of Kenya
1
Government of Lesotho
1
Government of Lesotho, World Health Organization (WHO) & United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF)
1
Government of Nepal Ministry of Education Department of Education
1
Government of Nepal, National Planning Commission
1
Government of Nepal, Ministry of Health
1
Government of Nepal, Ministry of Health and Population, National Centre for AIDS and STD Control
1
Government of Rwanda: Ministry of Health, Maternal and Child Health
1
Government of Sierra Leone
1
Government of Sierra Leone, Department for International Development, UN Population Fund, Irish Aid
1
Government of Sierra Leone, Ministry of Health and Sanitation Sierra Leone
1
Government of Sierra Leone, Ministry of Health and Sanitation, Health Education Division
1
Government of Sweden, Government of Switzerland, UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs
1
Government of the Netherlands
1
Government of the Republic of Malawi
1
Government of the Republic of Zambia
1
Governments of Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone
1
Govt. of the State of Palestine
1
Grace Musoke & Priscille Geiser
1
Grace, D.
1
Graves C. et al.
1
Grépin K.
1
Grépin, K.
1
Gribble RSF, Liese BH, Wickremsinhe MN
1
Grollman C.
1
Grotenhuis, R.
1
Group URD
1
Growth Analysis Studentplan
1
GSDRC
1
Gulani, A. & Sachdev, H.P.S
1
Guo B.
1
Gury S. et al.
1
H. Becher
1
H. Fuenzalida
1
H. Garrison-Desany
1
H. Sloot
1
H.Getahun
1
Haddad L., Verburg G., Fore H., et al.
1
Haefele-Abah, C.
1
Haid Haid
1
Haitham Shoman, Emilie Karafillakis and Salman Rawaf
1
Haja R. Wurie, Mohamed Samai and Sophie Witter, Human Resources for Health
1
Haldane, V., De Foo, C., Abdalla, S.M. et al.
1
Half of Syria
1
Hanlon et al.
1
Hann, K., Pearson, H., Campbell, D., et al.
1
Hariharan, N., Ishtiaq, A., Eldridge, C., et al.
1
Harm Reduction International
1
Harmer, Adele
1
Harvard Global Health Institute
1
Haver, Katherine
1
Hayc, SI.
1
Health and Education Advice and Resource Team
1
Health Policy Project, Futures Group
1
Health Policy Project, USAID
1
HEAT, UNICEF, Open University, AMREF
1
HEAT, UNICEF, Open University, AMREF, WHO
1
HelpAge
1
HelpAge International Myanmar, University of Public Health and University of Medicine-2
1
Helping babies breathe
1
Henry Perry
1
High-Level Panel on Humanitarian Financing Report to the Secretary-General
1
HIV
1
HIV Economics Reference Group
1
HIV Self-Testing Africa Initiative
1
Hivos people unlimited
1
hler, Oliver Razum, Jean-Olivier Schmidt
1
Hodge, Matthew
1
Hodgson, L. et al.
1
Hoffman, S.
1
Holly Young
1
Hotez, P.
1
Hotline in a Box
1
House of Commons International Development Committee
1
Housing Recovery and Reconstruction Platform – Nepal (HRRP)
1
Hoviyeh Afnan-Holmes, Moke Magoma, Theopista John, et al.
1
hrp human reproduction programme (research for impact)
1
HSRSP, RTI International
1
Huff, A.R.
1
Hugo Slim and Lorenzo Trombetta
1
Huihui Wang, Nathaniel Otoo, and Lydia Dsane-Selby
1
Humanitarian Accountability Partnership (HAP)
1
Humanitarian Advisory Group
1
Humanitarian Assistance and Resilience Programme Facility (HARP-F) & Myanmar Information Management Unit (MIMU)
1
Humanitarian Innovation Fund HIF
1
Humanitarian Practice Network
1
Humanitarian Practice Network (HPN)
1
Humanitarian Reponse Team
1
Humanity & Inclusion
1
Hynes W.
1
i-base
1
I. Eramova
1
I. Semini
1
IACAPAP
1
IACG Interagency Coordination Group on Antimicral Resistance
1
IATT
1
IAWG on Reproductive Health in Crises, IPPF, JSI, et al.
1
ICASO (International Council of AIDS Service Organizations)
1
icco (Partner to enterprising people)
1
ICRC
1
ICRC and International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies
1
ICRW ( International Center for Research on Women)
1
ICW Global (The International Community of Women Living with HIV/AIDS)
1
IDS
1
IFRC - International Federation of Red Cross/ Red Cresent Societies
1
ILEP International Federation of Anti-Leprosy Associations
1
ILGA-Europe (The European Region of the international Lesbian and Gay Association)
1
Ilkelezi et al.
1
ILO
1
ILO International Labour Organization
1
Ilona Kickbusch, Christian Franz, Anna Holzscheiter, Iris Hunger, Albrecht Jahn, Carsten Kö
1
IMA World Health
1
IMC Interrnational Medical Corps
1
Independent Observer of Global Fund
1
Independent Review Team
1
Indian Council of Medical Research & Department of Biotechnology
1
Ingrid Lewis and Sunit Bagree
1
Insecurity Insight
1
Institute for Public Policy Research
1
Institute for research in international assistance
1
Institute of Development Studies, Aga Khan University
1
Institute of Statistics Institute of Public Health
1
Institutional Repository for Information Sharing iris
1
Inter Sector Coordination Group (ISCG)
1
Inter-Agency Standing Commitee
1
Inter-Agency Standing Commitee (IASC)
1
Inter-Agency Task Team to Address HIV in Humanitarian Emergencies
1
Inter-agency Working Group on Reproductive Health in Crises
1
Inter-Parliamentary Union (For democracy, For everyone)
1
InterAction, The Rockefeller Foundation
1
Interagency Health and Nutrition Evaluations in Humanitarian Crises (IHE) Initiative
1
Interagency Task Team HIV in Humanitarian Emergencies
1
Internal Displacement Monitoring Center
1
Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre IDMC
1
International Alert
1
International Association for Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Allied Professions
1
International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
1
International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank
1
International Campaign to Ban Landmines
1
International Development Association
1
International Development Committee, Government of the United Kingdom
1
International Disability Alliance
1
International Disability and Development Consortium’s Inclusive Education Task Group
1
International Disablity and Development Consotrium (IDDC), UN
1
International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies
1
International Federation of Red Cross (IFRC)
1
International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies and the ICRC
1
International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC), Bangladesh Red Crescent Society (BDRCS)
1
International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC), World Health Organization (WHO)
1
International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, Geneva
1
International HIV/AIDS Alliance (Supporting Community Action on AIDS in Developing Countries)
1
International Initiative for Impact Evaluation (3ie)
1
International Institute for Environment and Development, Norwegian Refugee Council, International Rescue Committee, World Vision
1
International Institute of Rural Reconstruction, Give2Asia
1
International Journal for Equity in Health
1
International Journal of Health Policy and Management IJHPM
1
International Journal of Infectious Diseases
1
International Journal of Sociology and Anthropology
1
International Journal of Tubercolosis and Lung Disease
1
International Labor Organization (ILO)
1
International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI)
1
International Medical Corps
1
International Organization for Migration (IOM)
1
International Organization for Migration IOM
1
International Peace Institute
1
International Rescue Committee, et al.
1
International Review of the Red Cross
1
International Society for infectious Diseases
1
International Society of Nephrology
1
International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, World Health Organization
1
International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN), World Health Organization (WHO)
1
International Vaccines Task Force (IVTF)
1
Internationam Water and Sanitation Centre
1
IOM
1
IOM UN Migration IOM Somalia
1
Iosue, S.
1
IPPF (International Planned Parenthood Federation)
1
IPPF ESEAOR, UNFPA
1
IRC
1
Isabelle Risso-Gill and Leah Finnegan
1
ISDR
1
Islamic Relief
1
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, Ministry of Public Health
1
J. Amon
1
J. Ananworanich
1
J. Baer
1
J. Bear
1
J. Begovacc
1
J. Borghi
1
J. Butler
1
J. D. Lundgren
1
J. Dieleman, L. Singh et al.
1
J. E Wright, N. Aksee, et al.
1
J. E. Lawn
1
J. Klinte
1
J. Osborne
1
J. Peebles
1
J. Turner et al.
1
J. V. Lazarus
1
J. Vujcic, L.Blum, and P.K.Ram
1
J. W. Eaton
1
J.-G. Kühling
1
J.-W. De Neve
1
Jacksona, A.
1
Jacobson, J. et al
1
JAIDS Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes
1
James Darcy, Jessica Alexander, Maria Kiani et al.
1
Jan Egeland, Norwegian Institute of International Affairs
1
Jane Doherty
1
Jane Phiri and John E Ataguba
1
Jennifer Turner
1
Jeremy Shiffman
1
JIAS ( Journal of the International AIDS Society)
1
JICA
1
Jiménez, P.
1
Jindal, D.
1
Joachim Rüppel
1
Joe Schofield, Sarah Hess, Bandana Malhotra et al.
1
Joep Lange Institut
1
Johansson, Emily White
1
John Cosgrave and Margie Buchanan-Smith
1
John Cosgrave, Ben Ramalingam and Tony Beck
1
John Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
1
John Hopkins Bloomberg University
1
John Kinsman
1
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health , Syrian American Medical Society, et al.
1
Joint Learning Initiative on Faith & Local Communities
1
Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS)
1
Jolliffe, Kim
1
Jose Nkuni, Natasha Howard, Abraham Mnzava et al.
1
Joseph McCord, Emily Bancroft and Jessica Crawford
1
Joshi, M.P.
1
Journal of global health
1
Julia Samuelson, Rachel Baggaley, Gottfried Hirnschall et al
1
Jusot, V.
1
K. Slobodianiuk
1
K. Attawell
1
K. Boegel
1
K. Chkhatarashvili
1
K. Church
1
K. Elder
1
K. G. Andrews
1
K. Hauck
1
K. Kruja
1
K. Mangino
1
K. Safreed-Harmon
1
K. Seeher
1
K. Stone
1
K4D
1
Kadowa, Isaac
1
Kaiser Family Foundation
1
Kamali M, Munyuzangabo M, Siddiqui FJ, et al.
1
Kamali, M.
1
Kardan, A., O’Brien, C. and Masasa, M.
1
Karen Edmond, Rajiv Bahl, MD, PhD
1
Karen LeBan , Maryse Kok and Henry B. Perry
1
Karen Weidert, Amanuel Gessessew, Suzanne Bellet al.
1
Karin Hatzold
1
Kariuki S., K. H. Keddy, M. Antonio
1
Kasipo, Charles
1
Kate Kerber, Stefan Peterson & Peter Waiswa
1
Kates J,
1
Kates J.
1
Katz, R.
1
Kelsey Simmons, Zuki Mihyo and Lyn Messner
1
Kelsey Vaughan & Aradhana Thapa
1
Kenya Health Sector Strategic and Investment Plan (KNSSP)
1
Kenya Medical Research Institute
1
Kenya National Bureau of Statistics,National AIDS Control Council
1
KFF - Henry J Kaiser Family Foundation
1
Khan, Ayesha
1
Khuluza, F.
1
Kisanga O.
1
Klein O. et al
1
Klinkenberg, E
1
Klinkenberg, E. & Ochola, R.
1
Kondowe, K. et al.
1
Konrad-Adenauer-Stiftung
1
Korenromp E.
1
Kotzé, H.
1
Kraemer, J.
1
Kraus J. et al.
1
Krause, S.
1
Kristian Stokke, Roman Vakulchuk, Indra Øverland
1
Kumar, M.
1
Kurowski, C.
1
L. Arregoces
1
L. Crigler, et al.
1
L. Davies
1
L. Hertel
1
L. Khotenashvili
1
L. McGrory
1
L. Messner, L. Crye
1
L. Mofenson
1
L.Davies
1
Laech-Kemon, K.
1
Lancet 2017;
1
Lancet Glob Health
1
Lang, R
1
Langston, A., Weiss, J., Landegger, J., et al.
1
Leadership Managemtn & Governance project
1
Learning Route (LR), SUN (Scaling Up Nutrition)
1
LeBeau, D. & Yoder, P.S.
1
Leitner Center for International Law and Justice
1
LeMier, Ryan
1
Leuleseged Ageze, Hailu Zelelew, Habtamu Tadesse, et al.
1
Leveraging Essential Nutrition Actions to Reduce Malnutrition (LEARN)
1
Levy, Marcy, Veronica Magar, and Derrick Sialondwe
1
Lewis I
1
Li Z., Richter L., Lu C.
1
Liese B
1
Lili Mohiddin, Gabrielle Smith
1
LINKAGES, L., Regional Centre for Quality of Health Care, R. and United Nations Children's Fund , U.
1
Lipsky A., Mulaki A., Williamson T., et al.
1
Lisa Myers, Laura Theytaz-Bergman
1
Lloyd-Jones, Tony
1
Llyod, A.
1
LOGICA Study Series
1
LOGICA, HHI
1
Logistics Cluster World Food Programme WFP
1
London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine and CBM
1
London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and the Technische Universität München
1
Loua, A.
1
Lu C., Li Z.
1
Lu, C.
1
Lucinda Ramos
1
Lutherahjalpen/Church of Sweden
1
Luwabelwa, M.
1
Lynn Losert
1
M. Belfer
1
M. Cheng
1
M. Couldrey
1
M. Dallao
1
M. Dara, M. Grzemska, M. E. Kimerling, et al.
1
M. Doara, D. Choroliani, P. de Colombani
1
M. Gaanderse
1
M. Gutmann
1
M. Hammer
1
M. Hart
1
M. Herson
1
M. Higgins-Biddle
1
M. Hoekstra
1
M. L. Belfer
1
M. L. Mattingly
1
M. Manova
1
M. Marella and A. Robinson
1
M. Martinez-Alvarez et al.
1
M. Martínez-Álvarez et al.
1
M. Mireku,M. Kiruki, R. McCollum, et al.
1
M. Prescott, C. Boeke, T. Gotora, et al.
1
M. Ranganathan et al.
1
M. Ristola
1
M. SHOWKAT GANI et al.
1
M. SHOWKAT GANI, MAL ABIKA SARKER, BULBUL ASHRAF SIDDIQI, ILIA S MAHMUD,YAMIN TAUSEEF JAHANGIR, SA LLY THEOBALD, HERMEN ORM EL, SALAUDDIN BISWAS , KUHEL FAIZUL ISLAM, SUBORN A CAMELLIA, SABINA F AIZ RASHID
1
M. Slutsker
1
M. Vitoria
1
M. Ya Diul
1
M.-A. LeBlanc
1
M.A. Connolly, M. Gayer and S. Ottmani
1
M.Johnson
1
Mac-Seing, M.
1
Machalaba
1
Macro International
1
Makhashvili, N.
1
Malaria and Other Parasitic Diseases Division (MAL & OPD Division-RBC) [Rwanda] and ICF International
1
Malaria Consortium
1
Malaria Consortium South Sudan
1
Malaria Journal
1
Malawi Government
1
Malawi Human Rights Commission
1
Malcolm Clark
1
Mallick, Lindsay, Courtney Allen, and Rathavuth Hong
1
Mamdani M.
1
Manjula Marella
1
MapAction
1
March of Dimes
1
Margie Buchanan-Smith and John Cosgrave
1
Margie Buchanan-Smith and John Telford
1
Maria Isabel Egüez
1
Maria Neira, Edward Kelley, Mickey Chopra et al.
1
Maria Santamaria, Marie Bombin, Guitelle Baghdadi-Sabeti, et al.
1
Mariam Kirollos, Caroline Anning, Gunvor Knag Fylkesnes et al.
1
Marie Mercy Zevallos, et al.
1
Mario R Dal Poz, Neeru Gupta, Estelle Quain and Agnes LB Soucat
1
Markbreiter, J.
1
Martha Embrey, Marian Ryan, Edna Jamandre et al.
1
Martinez-Alvarez M.
1
Martinez-Alvarez M. et al
1
Martinez-Alvarez, M.
1
Marvin L. Birnbaum
1
Mary Florence Mukisa
1
Mary Keogh, Monika Brenes, Priska Gronenberg et al.
1
Mary Leakey et al.
1
Mary-Ann Waddell & Rob Aley
1
Maternal & Childhealth Advocacy International MCAI
1
Maternal and Child Health DirectorateFederal, Ministry of Health Ethiopia
1
Maternal and Child Health Integrated Program (MCHIP)
1
Maternal Health Division Department of Family Welfare Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Government of India
1
Maurice Bucagu, Jean M. Kagubare, Paulin Basinga, Fidèle Ngabo, Barbara K Timmons & Angela C Lee
1
Maurice T. Agonnoude, François Champagne, Nicole Leduc
1
Maxwell, D. & Burns, J.
1
McGuin, Rachael
1
McNamara N.
1
MCNV, Global Initiative on Psychiatry, and World Granny
1
ME Loeb, Arne H Eide
1
Measles Initiative
1
MEASURE
1
Medecins Sans Frontieres
1
Medecins Sans Frontieres (Access Campaign)
1
Medical Peace Work
1
Medina-Rincón, G.
1
Mediscript Ltd
1
medmissio and Action against AIDS Germany
1
Medmissio Institut
1
Mehtsun, Sinit
1
Melanie Duncan, et al.
1
Melissa Leach
1
Meyer, M.
1
mHealth Kenya
1
Micah et al.
1
Michelle Kooy, Leni Wild, Nat Mason et al.
1
Michigan State University, USAID
1
Mike Wessells
1
Millennium Development Goal Acceleration Initiative
1
Miller, C.
1
Minister for Medical Services
1
Ministère de la Santé Publique, Republique Démocratique du Congo
1
Ministry of Agricultur al Development (MOAD)
1
Ministry of Agricultural Development
1
Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Fisheries
1
Ministry of Disaster Management Affairs and Public Events
1
Ministry of Education, Nepal
1
Ministry of Education, Rwanda
1
Ministry of Finance and Economic Planning (MINECOFIN), Rwanda
1
Ministry of Gender and Family Promotion, Government of Rwanda
1
Ministry of Gender, Labour and Social Development, Uganda
1
Ministry of Health & Child Welfare
1
Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, India, et al.
1
Ministry of Health & Sanitation, Sierra Leone
1
Ministry of Health & Social Welfare India
1
Ministry of Health (MoH), Malawi and ICF International
1
Ministry of Health , World Health Organisation (WHO)
1
Ministry of Health [Kenya], National AIDS and STI Control Programme (NASCOP)
1
Ministry of Health and Child Welfare, Zimbabwe
1
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of India
1
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Directorate-General of Health Services, Mycobacterial Disease Control, National Tuberculosis Control Programme
1
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India
1
Ministry of Health and Population
1
Ministry of Health and Population, Ministry of Health, Nepal
1
Ministry of Health and Sanitation Sierra Leone
1
Ministry of Health and Sanitation, International Centre for Eye Health, Sightsavers
1
Ministry of Health and Social Services (MOHSS), UNAIDS
1
Ministry of Health and Social Services, Republic of Namibia
1
Ministry of Health and Social Services, Windhoek, Namibia
1
Ministry of Health and Social Welfare, Government of Lesotho
1
Ministry of Health Malawi
1
Ministry of Health Rwanda, The DHS Program, et al.
1
Ministry of Health The United Republic of Tanzania
1
Ministry of Health Uganda, Control of Diarrheal Diseases
1
Ministry of Health Uganda, NADIC, et al.
1
Ministry of Health Zambia
1
Ministry of Health, Republic of Fiji Islands
1
Ministry of Health, Botswana
1
Ministry of Health, Botswana;
1
Ministry of Health, Community Development, Gender, Elderly and Children
1
Ministry of Health, Gabarone, Botswana
1
Ministry of Health, Government of Kenya
1
Ministry of Health, Government of Lesotho
1
Ministry of Health, Government of Liberia
1
Ministry of Health, Ministry of Food and Agriculture, et al.
1
Ministry of Health, National Aids Control Council
1
Ministry of Health, Pakistan
1
Ministry of Health, Public Health Division
1
Ministry of Health, Republic of Liberia
1
Ministry of Health, Republic of South Africa
1
Ministry of Health, Repulic of Uganda
1
Ministry of Health, Rwanda & Rwanda Biomedical Centre
1
Ministry of Health, Tanzania
1
Ministry of Health, World Health Organisation (WHO), Roll Back Malaria
1
Ministry of Health, Zimbabwe
1
Ministry of Medical Services and Ministry of Public Health & Sanitation, Republic of Kenya
1
Ministry of National Health Services Regulations & Coordination Government of Pakistan
1
Ministry of Public Health, Afghanistan
1
Minja, N.W.
1
Misereor
1
Misereor, Brot für die Welt, GPF
1
Moe Aung
1
Monica de Castellarnau and Velina Stoianova
1
Moriana, S.
1
Morrison-Métois, Susanna
1
Morse S.
1
Move Humanity
1
Mpofu, M., Semo, B., Grignon, J., et al.
1
mPowering
1
MSEREOR, Brot für die Welt, Global Policy Forum Europe
1
MSF
1
msh
1
Msomi, N.
1
Muga R., Ndavi P., Kizito P. et al.
1
Mukhtar A Adeiza, Abdullah A Abba, Juliana U Okpapi
1
Muller, Helgard et al.
1
Murphy, Ben
1
Mursaleena Islam
1
Mwangi, Annabel
1
Myanmar, Ministry of Health and Sports
1
N. B. Karkara
1
N. Chowdhary, et al.
1
N. Drew
1
N. Ford
1
N. Maennling et al.
1
N. Singh et al.
1
N.V. Salabai
1
NACO
1
NACO, Department of AIDS Control
1
NAFIN (Nambia Alliance for Improved Nutrition)
1
Nakagaayi, D.
1
Nang Lao Liang Won (Researcher)
1
Nathalia Dukhan
1
Nathan J. Blanchet and Osei B. Acheampong
1
National Center for Tuberculosis and Leprosy Control, Cambodia
1
National Academy of Medical Sciences
1
National Agency for Control of AIDS (NACA)
1
National AIDS Authority
1
National AIDS Commission (NAC), Kingdom of Lesotho
1
National AIDS Commission (NAC), Republic of Liberia
1
National AIDS Commission Indonesia
1
National AIDS Commission of Liberia
1
National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO), Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India
1
National AIDS Control Organization (NACO), Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MOHFW), Government of India
1
National AIDS Council, Zambia
1
National AIDS Secretariat Sierra Leone, et al.
1
National Center for Tuberc ulosis and Leprosy Control (CENAT) , Cambodia
1
National Center for Tuberculosis and Leprosy Control (CENAT), Cambodia
1
National Center for Tuberculosis and Leprosy Control, Cambodia
1
National Centre for AIDS and STD Control
1
National Coordinating Agency for Population and Development , Ministry of Medical Services, Ministry of Public Health and Sanitation
1
National Coordination Committee, Jan Swasthya Sabha
1
National Health Accounts Technical Secretariat, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of india
1
National Health Mission
1
National Human Rights Commission
1
National Institute of Statistics of Rwanda and ICF International.
1
National Leprosy and Tuberculosis Control Program (NLTCP)
1
National Malaria Control Programme (NMCP) Communicable Disease Control Division Directorate General of Health Services Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Bangladesh
1
National Malaria Control Program (NMCP) [Liberia], Ministry of Health (MOH), Liberia Institute of Statistics and Geo-Information Services (LISGIS), and ICF
1
National Malaria Control Program - NMCP
1
National Malaria Elimination Centre, Ministry of Health, Zambia
1
National Population Commission (NPC
1
National Primary Health Care Development Agency, Abuja, Nigeria
1
National Primary Health Care et al.
1
National Public Health Institute of Liberia (NPHIL)
1
National Reproductive Health Programme Ministry of Health
1
National Statistical Office Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea, The DHS Program
1
National Statistics Office Manila, Philippines ICF Macro Calverton, Maryland, USA
1
National TB Control Program, Department of Health
1
National TB Control Programme, Bangladesh
1
National Tuberculosis and Leprosy Programme Ministry of Health and Social Welfare, Tanzania
1
National Tuberculosis Leprosy and Lung Disease Program (NTLD-program), Ministry of Health, Republic of Kenya
1
National Union of Disability Organisations of Rwanda (NUDOR)
1
NCD Alliance, IISD
1
Ncube, M.
1
NDP 2030
1
NEPAD
1
Nepal GHI Strategy
1
Nepal Ministry of Health and Population, New ERA, and ICF International
1
Net Hope
1
Network 100percent life
1
Network for Research, Learning & Action
1
New ERA
1
Newman et al
1
NFPA-UNICEF Joint Programme on Female Genital Mutilation/ Cutting (FGM/C)
1
NHSSP
1
Nidhi Singal
1
Nilar Tin et al.
1
Nisha Bhat, Peter H. Kilmarx, Freeman Dube, et al.
1
Noel G. Macalalad, Ma. Cecilia G. Ama, Arthur B. Lagos et al.
1
Nomad RSI Cambodia
1
Nomura S. et al.
1
Norwegian Church Aid and Presbyterian Disasters Assistance
1
Norwegian Institute of International Affairs
1
Norwegian Refugee Council NRC
1
NRC/The Camp Management Project (CMP)
1
NRSAD (National Religious Association for Social Development)
1
Nswilla A.
1
nternational Labour Organization
1
Nuclear Threat Initiative (NTI) and the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security (JHU)
1
Nugent, R.
1
Nunziata, K. R.
1
Nutrition Cluster
1
Nwokike J., Ludeman E., Thumm M.
1
O. Ajose
1
O. H. Okojie
1
O.M. Balakireva
1
Obichukwu I., Kennedy J., Harmer A.
1
OCSD, Social Development Department, Central and West Regions
1
ODI_ Humanitarian Policy Group
1
Odianose, Serena
1
OECD Publishing
1
OECD Publishing, Paris
1
Ogden Stephanie et al
1
Ogden, S.
1
Ogden, S., Gallo, K., Davis, S., et al
1
Okiro, EO.
1
One World Trust
1
Open Society Foundations
1
Open Society Initiative for Southern Africa (OSISA)
1
OpenLearn Create
1
Orange Health Consultants
1
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Eurostat and World Health Organization (WHO)
1
Organisation Mondiale de la Santé OMS
1
Oritz, G.
1
Overseas Development Institute (ODI)
1
Ovid
1
Oxfam International
1
Oxford Policy Management
1
Oxford Research Group
1
O’Connell, Meghan
1
P. Bayr
1
P. Booth
1
P. de Colombani, S. Ahmedov, K. Blondal, et al.
1
P. Drain, and T. Hall
1
P. E. Farmer et al.
1
P. Glaziou
1
P. Đurić
1
Padmani Mendi & Romi Gurung
1
Paina L. et al.
1
Palale M.
1
Palma, G.
1
Pan American Health Organization (PAHO)
1
Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), World Health Organization (WHO)
1
Pan American Health Organization PAHO
1
Pandit-Rajani, T., S. Sharma, and F. Muramutsa.
1
Panorma Perspectives
1
Patel V.
1
Paudel, D., A. Thapa, P. R. Shedain, and B. Paudel
1
People In Aid
1
Pepe VLE
1
PEPFAR;
1
PERC
1
Perez Calderon, Luis Jorge
1
Perry, H.
1
Petra G.H. Aarts
1
Pharmacy, Medicines & Poisons Board
1
Phone Myint
1
Physicians for Human Rights
1
Pierre André Michaud, Valentina Baltag, Venkatraman Chandra-Mouli et al.
1
Pigott, D. M.
1
Pinder, Étoile
1
Pinkstaff C.B.
1
Pinnock H
1
PITCH (Partnership to Inspire, Transform and Connect the HIV response)
1
Pitt C.
1
Pitt, C.
1
Pitt1, C.
1
Piva P., Dodd. R.
1
Plavgo, Ilze, Martha Kibur, Mahider Bitew, Tesfayi Gebreselassie, Yumi Matsuda, and Roger Pearson
1
PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases
1
PMC (US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health)
1
Pokhrel, Yog Raj
1
Polio Global Eradication Initiative
1
Pontifical Academy for Life
1
Population Council
1
Population Reference Bureau
1
Pothuis, Michal et al.
1
Potter, A.L., Vandy, M., Smart, N. Blanchet, K.l.
1
Poudel, BabuRam
1
Powell, Steve and others
1
Powell-Jackson, T.
1
Pradhan, Y.V., Upreti, S.R., Pratap, K.C.N, et al.
1
President's Malaria Initiative
1
President's Malaria Initiative et al.
1
President’s Malaria Initiative, CDC, MCHIP, MCSP
1
Prevent Project
1
Price, R.
1
Prisons Care & Counselling Association
1
Programme national de lutte contre le paludisme (PNLP) - Sénégal, Speak up Africa, PATH, Zero Malarian starts with me
1
Project Drawdown
1
Protection Cluster Save the Children The Alliance for Child Protection
1
Pryor, W.
1
PSA Tansforming The Supply Chain
1
Quirk, E.J.
1
R. Baggaley
1
R. Coker
1
R. Coninx
1
R. Edon
1
R. Elovich
1
R. Fransen-dos-Santos
1
R. Granich
1
R. H.Crespo, L. Ditiu, A. Kurats, etc al.
1
R. Knottneruset al.
1
R. Lessells, K. Mlisana and T. de Oliveira
1
R. L’Herminez
1
R. Nefdt, E. Ribaira and K. Diallo
1
R. Smart
1
R.S. Stephenson
1
R4V
1
Rachel Silverman
1
Rahman-Shepherd, A.
1
Rahul Shidhaye
1
Ramasamy, Selvaraju
1
Rana Y.
1
Rational Pharmaceutical Management Project
1
REACH - REACH Initiative
1
Reach Out
1
Reachout Consortium
1
Rebuilding Basic Health Services Project (RBHS)
1
Redfern, J. et al.
1
Rediscovering Biology
1
RedR UK
1
RedR UK and Tearfund
1
Refugee Studies Centre, University of Oxford
1
Refugee Study Centre
1
Refugees International
1
Refugees International (RI)
1
Regional Gender Task Force
1
Regional refugee & resilience plan in response to the Syria crisis
1
Renuka Bery, Sophie Boisson, Lizette Burgers et al.
1
REPFAR
1
REPOA
1
Repoductive Health Journal
1
Reproductive Health Matters
1
Republic of Bangladesh, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
1
Republic of Kenya Ministry of Health
1
Republic of Libera, Ministry for Health and Social Welfare
1
Republic of Liberia, Ministry of Health and Social Welfare
1
Republic of Malawi
1
Republic of Moldova South‐East European Region National Coordination Council
1
Republic of Rwanda
1
Republic of Rwanda: Ministry of Local Government, Ministry of Health & Ministry of Agriculture and Animal Resources
1
Republic of South Sudan
1
República Democrática de Timor-Leste
1
Research and reports in tropical medicine
1
Research Institute for Tropical Medicine National Tuberculosis Reference Laboratory
1
Research Triangle Institute (RTI) International
1
Restless Development
1
Richter, L., Foster, G. and Sherr, L.
1
Road map 2016 -2020
1
Roberts B.
1
Rose Zulliger
1
Ross-Degnan, D., Vialle-Valentin, C., and Briggs, J.
1
Routledge
1
Rubin D., O. K. Niang-Mbodj
1
Rubinyi, S.
1
Rune J. Simeonsson
1
Ruth Ayarza, Sophie Baver
1
Ruth Naylor
1
Rutstein, S.E., J. Ananworanich, S. Fidler, et al.
1
Rüppel, J.
1
Rüppel, T.
1
Rwanda Biomedical Center
1
Rwanda Biomedical Centre, Institute of HIV
1
Røttingen, J.A.
1
S.
1
S. Aleyan
1
S. Andersson, A. Heaton, et al.
1
S. Basu
1
S. Chynoweth, D. Quick et al.
1
S. Custer
1
S. E. Kellerman
1
S. F.Jakobsen
1
S. Feller
1
S. Ibisevic
1
S. Jain
1
S. Juneja
1
S. Laver
1
S. Lordemus
1
S. Richiedei
1
S. Song
1
S. Sweeney
1
S. Vermund
1
S. Warren
1
S.Kinloch-de Loës, et al.
1
SAARC Tuberculosis and HIV
1
Sabin Nsanzimana
1
Sachs, J.
1
Sachs, J., Karim, S., Aknin, L. et al.
1
Sachy, M
1
Safe the children
1
SAFOD & DFID
1
Sage Journals
1
Saiful Islam M. , Mizanur Rahman K., Sun Y., et al.
1
Saimiento, Juan Pablo et al.
1
Sameh Saleeb, Seydou Doumbia
1
Samuels, F., Amaya, A.B., Rodríguez Pose, R. and Balabanova, D.
1
Sandisan, P.
1
Sangath
1
Sangeeta Raja and Nadeem Mohammad
1
Sara Pantuliano
1
Save the Children (UK) South Africa Programme
1
Save the Children, Norway
1
Schäferhoff M.
1
Schmid B, Thomas E, Olivier J and Cochrane JR.
1
Schneider M. et al.
1
School Health Integrated Programming (SHIP)
1
Schot, Sander
1
Schrade, C.
1
Schubert L.
1
Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft
1
Schwienhorst, E.M.
1
Science Direct
1
Scientific and Cultural Organization
1
Scientific Data
1
Scott S.
1
Sean Healy and Sandrine Tiller
1
Searle, L.
1
SEEP Network
1
Sen Monorom
1
Serneels, P. & Lievens, T.
1
Seth Mnookin
1
Sethi, T.
1
Sexual and Reproductive Health Matters (SRHM)
1
SFU MPH Capstone Project
1
Shahnaz Arshad
1
Sharma, Mahasharm
1
Shekhar Saxena and Preston J. Garri
1
Shoaib Fahad Hussai, Peter Boyle, Preeti Patel and Richard Sullivan
1
Shotton J.
1
Shroff Z.
1
Sian Tesni and Anais Keenon
1
Sibanda-Mulder, Flora
1
Sida
1
Sider, R. , Buswell, M. , Al Salman, M. et al.
1
Sierra Leone Government, Ministry of Health and Sanitation
1
Sierra Leone Government, National HIV and AIDS Secretariat
1
Sierra Leone Red Cross Society
1
Sightsavers, Department for International Development, The International Trachoma Initiative , et al.
1
Sigmund Freud Privatuniversität
1
Silva, S.
1
Singh, Iesha
1
Snow, RW.
1
Socieux
1
Sohaib Athar
1
Sophie Witter, Nouria Brikci, Tim Harris, et al.
1
South African Government
1
South African National AIDS council (our Action count)
1
South African National AIDS Council, et al.
1
South Sudan Public Health Emergency Operations Center (PHEOC)
1
Southern African Development Community
1
Sparkes S.
1
Sphere
1
Spigel, Lauren
1
Spiro D., Devkota M., Rana P. et al.
1
Springer Science+Business Media
1
SSRC
1
Standing committee on Nutrition SCN, et al.
1
Standleya C. J., Carlinb E. P., Sorrella E. M. et al.
1
Start Fund
1
Start Network
1
STAT.KG
1
Steekelenburg, E. V. et al.
1
Steele, Andre
1
Stefan Mauss, et al.
1
Stender, Stacie
1
STEPS Centre, Institute of Development Studies
1
Steve Aldrich, et al.
1
Steve Peat
1
Stoddard, Abby
1
Stop TB Partnership to reach
1
Stop TB Partnership. Working Group on TB
1
Strange A. et al.
1
Strange, A.
1
Strange, A. M.
1
Strategic Executive Group and Partners
1
Strengthening Pharmaceutical Systems (SPS) Program
1
Suárez, C., Nolder, D., García-Mingo, A. et al.
1
Sundewall, J.
1
Supriya Akerkar and Rhea Bhardwaj
1
Susan Nicolai and Carl Triplehorn
1
Syrian American Medical Society
1
Syrian American Medical Society Foundation
1
T. Abdullaev
1
T. Chitashvili, S. Holschneider, O. Annie Clark
1
T. Islam, T. Hiatt, C. Hennig, et al.
1
T. Leonhardt
1
T. Lievens
1
T. Zardiashvili
1
Tabarovsky, I.
1
Tanabe M. et al.
1
Tanzania Ministry of Health, Community Development, Gender, Elderly and Children.
1
Tarun Gera, Dheeraj Shah, Paul Garner et al.
1
TB Alliance
1
TB online
1
TB/CTA
1
TDH
1
Tearfund
1
Technology Transfer and Research Translation Directorate of the Ethiopian Public Health Institute
1
Terre des hommes, Save the Children, Plan International, SOS Children's Villages International, World Vision, ChildFund Alliance
1
Thacher, Emily
1
Than Tun Sein
1
The Asia Foundation
1
The Assessment Capacities Project and Emergency Capacity Building Project
1
The Audit Service Sierra Leone
1
The British Medical Journal (BMJ)
1
The Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics & Policy CDDEP
1
The Chatham House
1
The Child Protection Initiative, Save the Children
1
The Coalition for Children Affected by AIDS
1
The Department of Social Development
1
The DHS Program
1
The DHS Program ICF International
1
The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU)
1
The Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Ministry of Health
1
The Global Public Private Partnership for Handwashing
1
The Government of Malawi
1
The Government of the Republic of Zambia
1
The Governments of Burkina Faso and Norway, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, and the World Bank Group
1
The International Monetary Fund, World Bank Group, World Health Organization, et al.
1
The Lancet Commissions
1
The Ministry of Labour, Health and Social Affairs of Georgia
1
The Montpellier Panel
1
The Partnership for Maternal, Newborn & Child Health
1
The Polio Global Eradication Initiative
1
The Republic of Malawi
1
The Republic of Montenegro
1
The Republic of Tajikistan
1
The Republic of the Union of Myanmar, Ministry of Health
1
The Republic of the Union of Myanmar, Ministry of Health and Sports, Department of Health
1
The Republic of the Union of Myanmar, Ministry of Health and Sports, Department of Medical Research, Department of Public Health, Department of Medical Care, UNFPA
1
The Republic of the Union of Myanmar, Ministry of Health and Sports, Department of Public Health, Child Health Division
1
The Republic of the Union of Myanmar, Ministry of Health and Sports, Department of Public Health, Department of Medical Services and UNFPA
1
The Strengthening High Impact Interventions for an AIDS-free Generation (AIDSFree) Project
1
The Tuberculosis Coalition for Technical Assistance (TBCTA)
1
The United States President's Emergency Plan For Aids Relief
1
The University of Reading
1
The William J. Clinton Foundation
1
The World Bank
1
The World Bank Group
1
The World Bank, et al.
1
Thomas, M. and Ninomiya, A.
1
Thomson, D., Shivanandan, J. & Brown, T.
1
Thomson, D., Shivanandan, J. &
1
Thomson, M.C.
1
Ties Boerma, Colin Mathers, Carla AbouZahr, Somnath Chatterji, Daniel Hogan and Gretchen Stevens
1
Titus, M., Hendricks, R., Ndemueda, J., McQuide, et al
1
Todd G.
1
Tom Corsellis and Antonella Vitale
1
Tonelli, M.
1
Torres-Rueda S.
1
Towards a Safer World
1
Transparency International Ukraine
1
Trinidad D.
1
Tromp, J.
1
Tropical Diseases Research Centre, Zambia, DHS
1
Tufts University, Oxfam
1
Turner, Jennifer, and Bryan Burgess
1
Tylor & Francis
1
U. Laukamm-Josten
1
u.r.d.
1
U.S. Agency for International Development
1
U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
1
U.S. Global Malaria Coordinator
1
U.S. President’s Malaria Initiative (PMI), CDC, USAID, et al.
1
UCL
1
UCL Institute for Global Health and Development Education Research Centre, Institute of Education
1
Uganda Aids Commission, Republic of Uganda
1
Uganda Government (OPM)
1
Uganda Ministry of Health
1
Uganda National Action on Physical Disability (UNAPD)
1
UHC2030
1
UKaid
1
UKAid, CRS
1
Ukrainian Institute for Social Research after Olexander Yaremenko
1
UN Convention to Combat Desertification
1
UN Development Programme, The Global Cluster for Early Recovery
1
UN Development Programme, UN High Commissioner for Refugees
1
UN Development Programme, UN Mission for Ebola Emergency Response
1
UN Enivronemnt Programme UNEP
1
UN General Assembly
1
UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNCHR)
1
UN High Commissioner for Refugees UNHCR, TANGO
1
UN Mission for Ebola Emergency Response
1
UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, UN Country Team in Yemen
1
UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, UN Resident Coordinator for Mozambique, UN Country Team in Mozambique
1
UN Partnership to Promote Rights of People with Disabilites
1
UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East
1
Un Security Council
1
UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN)
1
UN Women, UNFPA
1
UN-Habitat
1
UNAIDS (Joint United Nations Programme on HIV
1
UNAIDS, et al.
1
UNAIDS, The National AIDS Authority (NAA)
1
UNAIDS, UNICEF
1
UNAIDS, UNODC (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime)
1
UNCEF
1
UNDAF Ghana
1
UNDP (United Nations Development Programme)
1
UNDP, IRGT, UNFPA, UNAIDS, WHO, USAID, PEPFAR, UCSF Center of Excellence for Transgender Health, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
1
UNESCO
1
UNESCO Publishing (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization)
1
UNESDOC Digital Library
1
UNFPA (United Nations Population Fund)
1
UNFPA, Save the Children USA
1
UNHCR The UN Refugee Agency
1
UNHCR United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees
1
Unicef (Eastern and Southern Africa Office)
1
Unicef (United Nations Children’s Fund)
1
UNICEF Bangladesh
1
UNICEF Kosovo in cooperation with Kosovo Health Foundation
1
UNICEF Programme Division
1
UNICEF Regional Office for Central and Eastern Europe and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CEECI)
1
UNICEF Sudan
1
UNICEF Supply Division
1
UNICEF Uganda
1
Unicef, Ministry of Gender, Labour and Social Development, The Republic of Uganda
1
UNICEF, WHO
1
UNICEF, WHO, Wellstart International
1
UNICEF, World Food Programme (WFP)
1
Unicef, World Health Organization
1
UNICEF/AMREF
1
Unitaid (Innovation in Global Health), World Health Organization (WHO)
1
United Nations Development Programme Iraq (UNDP)
1
United Nations - Environment Management Group (EMG)
1
United Nations agencies, the World Bank and the European Commission
1
United Nations and Partners
1
United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN)
1
United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), World Health Organization (WHO)
1
United Nations Children’s Fund UNICEF
1
United Nations Educational
1
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organizations (UNESCO), Bangkok
1
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR)
1
United Nations Industrial Develoopment Organization
1
United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific (ROAP)
1
United Nations Population Fund
1
United Nations Population Fund UNFPA
1
United Nations System in Uganda
1
United Nations UN
1
United Nations University
1
United States Agency for International Development (USAID), SIAPS
1
United States Government Zambia Interagency Team
1
Uniting Combat Negleceted Tropical Diseases
1
University of Buffalo
1
University of Cambridge
1
University of Cambridge shelterproject
1
University of Oxford
1
University of Zambia
1
US Agency for International Development
1
US Embassy Freetown
1
USAI
1
USAID (U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief)
1
USAID ASSIST Project
1
USAID Deliver Project
1
USAID From the American People
1
USAID | DELIVER PROJECT, Task Order 4
1
USAID, SPS, Strengthening Pharmaceutical Systems Program-Kenya
1
USAID, CDC
1
USAID, Deliver Project
1
USAID, FHI360, VALID, et al.
1
USAID, Health Finance & Governance
1
USAID, Health Policy Project
1
USAID, JSI Research and Training Institute, fhi
1
USAID, MCHIP
1
USAID, MOH (Nepal)
1
USAID, SIAPS
1
USAID, SIAPS (Systems for Improved Access to Pharmaceuticals and Services)
1
USAID, Stop TB Partnership
1
USAID, StopTBPartnership
1
USAID, Strengthening Pharmaceutical Systems SPS
1
USAID, UNICEF, UNFPA
1
USAID/E&E/DGST, Creative Associates International & JBS International
1
USAIDS BASICS Project
1
V. Andreeva
1
V. Cambiano
1
V. Habiyambere
1
V. Ilyenkova
1
V. J. Wirtz
1
V. Patel
1
van Ek, Vera
1
Van Ledden, M.
1
Van PraagO.
1
van Voren, R.
1
Vassall A.
1
Vassall, A.
1
Vatican COVID-19 Commission
1
Vigaud-Walsh, Francisca
1
Ville de Goyet, Claude de
1
Villella, Christina
1
WACD
1
WACD West Africa Comission on Drugs
1
Wageningen University
1
Wambugu, Samuel
1
Wang, S., N. Hoohlo, I. Tshabalala, K. Ntoi, and T. Sepetla
1
Wang, Wenjuan, Gheda Temsah, and Emily Carter
1
Wapling, L.
1
War Child
1
Wardlaw, Tessa M.
1
Warsame A.
1
WarTrauma Foundation
1
Washington, DC: Palladium, Health Policy Plus
1
Water Partnership Program
1
WaterAid
1
WE Consult
1
Webb, D.
1
Welburn S. C., Beange I. et al
1
Wenjuan Wang, Rebecca Winter, Lindsay Mallick, Lia Florey, Clara Burgert-Brucker, and Emily Carter
1
Wexler A.
1
WFP
1
WHO et. al
1
WHO Regional Office for Africa
1
WHO, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, and the International Trachoma Initiative
1
WHO, UNFPA, and Escuela Andaluza de Salud Publica Consejeria de Salud
1
WHO, USAID, UNICEF
1
Willcox et al
1
Willott C et al.
1
Willy McCourt, W. & Awases, M.
1
Wilson, Dave
1
Wilton Park
1
Winter, Rebecca, Jennifer Yourkavitch, Lindsay Mallick, and Wenjuan Wang
1
Women's Refugee Commission
1
Women's Refugee Commission (WRC) and UNICEF Lebanon
1
Women's Refugee Commission, IAWG
1
Women’s Refugee Commission
1
Word Health Organization
1
Working Group on Sustainable Financing
1
World Bank et al.
1
World Bank Group Staff
1
World Bank Group, and World Health Organization WHO
1
World Bank, et al.
1
World Bank, GFDRR
1
World Diabetes Foundation
1
World Economic Forum et al.
1
World Federation for Mental Health
1
World Federation for Mental Health (WFMH)
1
World Health Organization (WHO), Regional Office for South-East Asia
1
World Health Organisation (WHO) Country Office for Nepal
1
World Health Organisation (WHO) Regional Office Africa
1
World Health Organisation (WHO) Regional Office for Africa
1
World Health Organisation, International Labour Organization
1
World Health Organization ( WHO), Regional Office for Africa
1
World Health Organization (Africa)
1
World Health Organization (South-East-Asia)
1
World Health Organization (TB/HIV Working Group)
1
World Health Organization (Western Pacific Region)
1
World Health Organization (WHO) and DOH Philippines
1
World Health Organization (WHO), Country Office for Myanmar
1
World Health Organization (WHO), UNICEF
1
World Health Organization (WHO), Alliance for Health Policy and Systems Research
1
World Health Organization (WHO), Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse
1
World Health Organization (WHO), Inter-Agency Task Team (IATT), UNICEF
1
World Health Organization (WHO), Kenya Country Office
1
World Health Organization (WHO), Regional Office for South-East Asia
1
World Health Organization (WHO), The Global Fund, Gavi et al.
1
World Health Organization and Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation
1
World Health Organization Eastern Mediterranean
1
World Health Organization WHO (Africa)
1
World Health Organization WHO, Bangladesh
1
World Health Organization WHO, et al.
1
World Health Organization WHO, Regional Office Africa Region
1
World Health Organization WHO, Regional Office African Region
1
World Health Organization WHO, Western Pacific Region
1
World Health Organization, Stop TB Partnership
1
World Health Organization, Global Polio Eradication Initiative
1
World Health Organization, IASC
1
World Health Organization, Regional Office for Africa. Ministry of Health, Botswana
1
World Health Organization, Regional Office for Europe
1
World Health Organization, Regional Office for South-East Asia
1
World Health Organization, Regional Office for South-East Asia, Health Situation and Trend Assessment Unit of Health System Department
1
World Health Organization, South-East Asia
1
World Health Organization, UNICEF
1
World Health Organization, Western Pacific
1
World Health Organization, Western Pacific Office
1
World Humanitarian Summit
1
World Palliative Care Alliance
1
World Psychiatric Association
1
World Vision, International Research Institute for Climate and Society
1
WPSAR
1
Xu K., Soucat A., Kutzin J., et al.
1
Y. Santa-Ana-Tellez et al.
1
Y. W. Olagbuji
1
Yamey G.
1
Yan I.
1
Yaron, Gil
1
Young, H., Marshak, A.
1
Youth Rise (for reducing drug related harm)
1
Z. C. Shroff et al.
1
Z. Jarrah, A. Lee, K. Wright, K. Schulkers, D. Collins
1
Z. T. Gavry
1
Zachary, Blake, Zhuzhi Moore, and Pav Govindasamy
1
Zaidi, Shehla
1
Zedbooks
1
Zimbabwe National Statistics Agency (Z IMSTAT) and ICF International. 20
1
Zimbabwe, Ministry of Health and Child Care
1
Publication Years
2020-2026
427
2010-2019
1381
2000-2009
180
1990-1999
8
Category
Countries
852
Key Resources
126
Public Health
87
Women & Child Health
86
Clinical Guidelines
55
Capacity Building
19
Pharmacy & Technologies
10
General Guidelines
1
Toolboxes
HIV
190
Health Financing Toolbox
125
TB
96
Conflict
89
COVID-19
85
Disability
75
Mental Health
61
Ebola
60
Natural Hazards
51
Planetary Health
45
Rapid Response
42
Global Health Education
37
Pharmacy
32
AMR
31
NTDs
29
Refugee
24
Polio
19
Caregiver
18
NCDs
15
Cholera
6
Typhoon
4
Social Ethics
3
Health Financing
3
Zika
2
Specific Hazards
2
Report V of Conversations on Planetary Health
Background: The last decade has seen a dramatic increase in international and domestic funding for malaria control, coupled with important declines in malaria incidence and mortality in some regions of the world. As the ongoing climate of financial
...
uncertainty places strains on investment in global health, there is an increasing need to audit the origin, recipients and geographical distribution of funding for malaria control relative to populations at risk of the disease. Methods: A comprehensive review of malaria control funding from international donors, bilateral sources and national governments was undertaken to reconstruct total funding by country for each year 2006 to 2010. Regions at risk from Plasmodium falciparum and/or Plasmodium vivax transmission were identified using global risk maps for 2010 and funding was assessed relative to populations at risk. Those nations with unequal funding relative to a regional average were identified and potential explanations highlighted, such as differences in national policies, government inaction or donor neglect.
more
Background: A recent report by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) highlights that mental health receives little attention despite being a major cause of disease burden. This paper extends previous assessments of development assistance for mental health (DAMH) in two significant w
...
ays; first by contrasting DAMH against that for other disease categories, and second by benchmarking allocated development assistance against the core disease burden metric (disability-adjusted life year) as estimated by the Global Burden of Disease Studies. Methods: In order to track DAH, IHME collates information from audited financial records, project level data, and budget information from the primary global health channels. The diverse set of data were standardised and put into a single inflation adjusted currency (2015 US dollars) and each dollar disbursed was assigned up to one health focus areas from 1990 through 2015. We tied these health financing estimates to disease burden estimates (DALYs) produced by the Global Burden of Disease 2015 Study to calculated a standardised measure across health focus areas—development assistance for health (in US Dollars) per DALY.
more
Financing for malaria control has increased as part of international commitments to achieve the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). We aimed to identify the unmet financial needs that would be biologically and economically equitable and would increase the chances of reaching worldwide malaria-contr
...
ol ambitions.
more
The definition of Official Development Assistance (ODA) has for 40 years been the global standard for measuring donor efforts in supporting development co-operation objectives. It has provided the yardstick for documenting the volume and the terms o
...
f the concessional resources provided, assessing donor performance against their aid pledges and enabling partner countries, civil society and others to hold donors to account. Yet for all its value, the ODA definition has always reflected a compromise between political expediency and statistical reality. It is based on interpretation and consensus and therefore allows for flexibility. It has evolved over the decades, while preserving the original concepts of a definition based on principal developmental motivation, official character and a degree of concessionality. While agreement on the ODA concept was a major achievement, discussion of the appropriateness of this measure has never ended. The paper documents the evolution of the ODA concept and proposes a possible new approach to measuring aid effort.
more
The most significant finding of the case study for integrating antimicrobial resistance (AMR)into existing programs and mobilising resources for funding in Nigeria, is that most of the AMR activities within the Nigerian National Actio
...
n Plan (NAP)canalready be incorporated within existing programs of the Federal Ministry of Health (FMOH), Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (FMARD) and their agencies or institutes. Certain programs and initiatives already have an AMR element incorporated or could,with little effort,include some additional AMR actions, however much is already being planned and has started with existing federal funding and existing staffing and other resources including development partner support and is being driven by significant political will from the ministries as well as implementation support from the Nigerian Centers for Disease Control as the focal point.
more
Research Article
PLOS ONE | DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0169530 February 16, 2017
In September 2021, the UN and its partners presented a response plan to mitigate the impact of the water crisis in northern and north-east Syria which requested US$200 million to assist up to 3.4 million of the over five million people estimated to be affected by the water crisis in northern Syria b
...
etween September 2021 and February 2022. Under the auspices of the 2022-2023 Syria Humanitarian Response Plan, this updated water response plan presents the most recent needs based on latest forecasts and is a continuation of the earlier plan presented in 2021. It covers the needs from all response modalities/areas1 for Syria, aims to assist 5 million people until December 2022 and requests $226.2 million.
more
Progress in tuberculosis control worldwide, including achievement of 2015 global targets, requires adequate financing sustained for many years. WHO began yearly monitoring of tuberculosis funding in 2002. We used data reported to WHO to analyse tube
...
rculosis funding from governments and international donors (in real terms, constant 2011 US$) and associated progress in tuberculosis control in low-income and middle-income countries between 2002 and 2011. We then assessed funding needed to 2015 and how this funding could be mobilised.
more
Background
Four methods have previously been used to track aid for reproductive, maternal, newborn, and child health (RMNCH). At a meeting of donors and stakeholders in May, 2018, a single, agreed method was requested to produce accurate, predictable, transparent, and up-to-date estimates that coul
...
d be used for analyses from both donor and recipient perspectives. Muskoka2 was developed to meet these needs. We describe Muskoka2 and present estimates of levels and trends in aid for RMNCH in 2002–17, with a focus on the latest estimates for 2017.
Methods
Muskoka2 is an automated algorithm that generates disaggregated estimates of aid for reproductive health, maternal and newborn health, and child health at the global, donor, and recipient-country levels. We applied Muskoka2 to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development's Creditor Reporting System (CRS) aid activities database to generate estimates of RMNCH disbursements in 2002–17. The percentage of disbursements that benefit RMNCH was determined using CRS purpose codes for all donors except Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance; the UN Population Fund; and UNICEF; for which fixed percentages of aid were considered to benefit RMNCH. We analysed funding by donor for the 20 largest donors, by recipient-country income group, and by recipient for the 16 countries with the greatest RMNCH need, defined as the countries with the worst levels in 2015 on each of seven health indicators.
Findings
After 3 years of stagnation, reported aid for RMNCH reached $15·9 billion in 2017, the highest amount ever reported. Among donors reporting in both 2016 and 2017, aid increased by 10% ($1·4 billion) to $15·4 billion between 2016 and 2017. Child health received almost half of RMNCH disbursements in 2017 (46%, $7·4 billion), followed by reproductive health (34%, $5·4 billion), and maternal and newborn health (19%, $3·1 billion). The USA ($5·8 billion) and the UK ($1·6 billion) were the largest bilateral donors, disbursing 46% of all RMNCH funding in 2017 (including shares of their core contributions to multilaterals). The Global Fund and Gavi were the largest multilateral donors, disbursing $1·7 billion and $1·5 billion, respectively, for RMNCH from their core budgets. The proportion of aid for RMNCH received by low-income countries increased from 31% in 2002 to 52% in 2017. Nigeria received 7% ($1·1 billion) of all aid for RMNCH in 2017, followed by Ethiopia (6%, $876 million), Kenya (5%, $754 million), and Tanzania (5%, $751 million).
Interpretation
Muskoka2 retains the speed, transparency, and donor buy-in of the G8's previous Muskoka approach and incorporates eight innovations to improve precision. Although aid for RMNCH increased in 2017, low-income and middle-income countries still experience substantial funding gaps and threats to future funding. Maternal and newborn health receives considerably less funding than reproductive health or child health, which is a persistent issue requiring urgent attention.
Funding
Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation; Partnership for Maternal, Newborn & Child Health.
more
Street Child & Child Protection AoR: Accelerating localised response to COVID-19: Practical pathways
The COVID-19 pandemic presents a rare and immediate opportunity for a norm shift towards localisation in the humanitarian architecture. Whils tinternational humanitarian actors are facing constraints in funding and restrictions on mo
...
vement and travel, national and local level humanitarian actors are on the ground to respond. A timely investment in localcapacities and capabilities creates a strong platform for effective, efficientand sustained response and recovery from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in the days, months and years ahead.
more
Technical meeting to support Ebola affected countries on the recovery and resilience plans with a focus on GAVI, the Global Fund and other partners' funding - Report, 9-11 June 2015
World Health Organization
(2015)
The objectives of the meeting were to agree on coordinated and aligned support to the 3 countries’ national health recovery plans (Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone); to identify cross-cutting areas and opportunities for integration; to identify ways to improve implementation modalities; and to identi
...
fy actions including technical assistance needed to support the countries in the process of building resilient health systems.
The outcomes of the meeting consisted in proposed country action plans to move forward with the implementation of the recovery plans. The action plans includes:priorities and areas of work; activities needed to improve implementation modalities; technical assistance needs.
more
The Cost of Security Risk Management for NGOs explores the costs related to safety and security management for aid programmes. It aims to assist all aid practitioners to determine their risk management expenditure more accurately, and demonstrate an evidence-based approach when presenting this infor
...
mation to donors.
The paper will be particularly relevant to those responsible for programme planning and management, donor proposal writing, as well as safety and security risk management.
more
Report on the PCB Bureau on UNAIDS' funding situation based on the recommendations of the informal multistakeholder task team
In 2015 around 15 million people living with HIV were receiving antiretroviral treatment (ART) in sub–Saharan Africa. Sustained provision of ART, though both prudent and necessary, creates substantial long–term fiscal obligations for countries affected by HIV/ AIDS. As
...
donor assistance for health remains constrained, novel financing mechanisms are needed to augment funding domestic sources. We explore how Innovative Financing has been used to co–finance domestic HIV/AIDS responses. Based on analysis of non–health sectors, we identify innovative financing instruments that could be used in the HIV response.
more
While much progress has been achieved over the past year, the Region of the Americas has stubbornly remained the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic. PAHO is launching its 2021 COVID-19 Response Strategy and Donor Appeal to continue supporting Latin
...
American and Caribbean countries and territories in their fight against COVID-19. This document outlines PAHO’s regional strategy for the year 2021 to sustain and scale-up the response to COVID‑19 pandemic in the Americas, suppress the community transmission of the virus and mitigate the longer-term health impact of the pandemic.
US$ 239 million is needed to support critical response efforts in the Americas between 1 January and 31 December 2021
more