Filter
515
Featured
67
18
Language
Document type
184
157
49
46
37
13
10
6
6
3
2
1
1
Countries
57
20
18
16
14
11
11
10
9
8
8
8
7
7
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
193
50
40
35
10
8
4
Toolboxes
244
40
25
21
18
16
14
12
10
10
8
8
8
6
4
3
2
2
1
This guidance addresses rationale, risk-based scenarios, practical considerations prior to adoption of the self-testing products, quality assurance, safety and ethical considerations, and data manag
...
What is the guidance for vaccination of women with breastfeeding infants, women who are pregnant or planning to get pregnant and women who are menstruating? What about vaccines and fertility? WHO’
...
The ISUOG President and Board of Trustees express their sympathy, encouragement and support towards all health professionals fighting the COVID-
...
Instructional Manual for the care of pregnant and postpartum women in the context of the covid-19 pandemic
Este Manual de Recomendações para a A
...
This publication provides recommendations for the management of critically ill adult patients with COVID-19 being treated in intensive care units (ICUs) in the Americas. These clinical practice guid
...
-Covid-19 и беременность
-Особенности применения методов диагностики у беременных
-Особенности лечения
...
This guidance is targeted to primary health care policy-makers and only addresses issues relevant for primary health care providers. It has been prepared on the basis of a systematic review of the best available evidence
...
COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy is currently one of the main obstacles to worldwide herd immunity and socioeconomic recovery. Because vaccine coverage c
...
An overview of COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca and why it is authorised in the EU. Available in 22 languages
18 Febr. 2021
The following print-only materials are developed to support COVID-19 recommendations. All materials are free for download. They may be printed on a standard office printer, or you may use a commerci
...
The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated and added yet another layer of vulnerability to an already dire web of vulnerabilities of girls in the Africa
...
SARS-CoV-2 infections among children and adolescents cause less severe illness and fewer deaths compared to adults. While a less severe course of infection is a positive outcome, there are concerns
...
This document summarizes preparedness and response activities to address the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak in South Sudan through the end
...
Guidance for General Medical and Specialised Mental Health Care Settings
The World Health Organization invites clinicians and patients to collect information on COVID-19 in a systematic way
...
The guide explains how vaccines work and answers your common questions as well as providing up-to-date information on the current approved COVID-19
...
This guideline is for:
• health and care practitioners
• health and care staff involved in planning and delivering services
• commissioner
...
A series of data syntheses from the RCCE Collective Service. It focuses on public perceptions of the COVID-19 vaccinations, bringing together 66 data sources from quantitative surveys across 107 cou
...
In the present report, the Special Rapporteur on the sale and sexual exploitation of children, including child prostitution, child pornography and other child sexual abuse mate
...
Background paper 9
The Independent Panel for Pandemic Preparedness and Response
May 2021
Nigeria reported its first case of COVID-19 at the end of February 2020 and subsequently experienced
four waves, with peaks in June 2020
...
The Government of Republic of Zambia reported the first confirmed cases of COVID-19 on 18th March 2020. As of April 27th, 2020, there were 89 confirmed cases, three deaths
...
The Government of Republic of Zambia reported the first confirmed cases of COVID-19 on 18th March 2020. As of April 27th, 2020, there were 89 confirmed cases, three deaths
...
The crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated preexisting structural economic inequalities, and had a disproportionate impact on informal
...
Mapping of Communication Resources COVID-19
recommended
This resource mapping contains signposting and direct links to a range of resource sites and content online; this includes information about the main sources for trustworthy information about the pa
...
Sudan recorded the first COVID-19 case on 13 March 2020 and, at the beginning of July, the Federal Ministry of Health had confirmed that nearly 10,
...
Conflict, climate crisis and COVID-19 pose great threats to the health of women and children.
Manufacturers:
SK Bioscience Co. Ltd. [COVID-19 Vaccine (ChAdOx1-S [recombinant])]
Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd. [COVISHIELD™, ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Corona Virus Vaccine (Recombinant)]
...
April 2020
This Guidance Note offers a list of recommendations based on a combination of WHO guidelines, good practice and expert advice based on the latest scientific research. The situation with COVID
...
In India, in response to the above and guided by our counterparts in the government of India, the UN agencies have developed the Novel Coronavirus Disease Joint Health Response Plan by UN Agencies and
...
9 Febr. 2022
The COVID Covovax™ (SIIPL) and Nuvaxovid™ (Novavax) vaccine explainer includes key vaccine specific information on the vaccine specific requirements.
The objective of Health in the Americas: Overview of the Region of the Americas in the Context of the COVID-19 Pandemic is to respond to the need to address important public health issues in an incr
...
22 December 2020
The COVID-19 vaccine safety guidance manual has been developed upon recommendation and guidance of GACVS members, as well as by
...
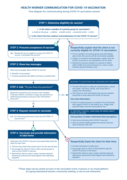
13 May 2021 The diagram supports health workers by outlining key steps and messages to communicate during a COVID-19 vaccination session.
Across Zimbabwe, 7 million people in urban and rural areas are in urgent need of humanitarian assistance, compared to 5.5 million in August 2019. Since the launch of the Revised Humanitarian Appeal in August 2019, circumstances for millions of Zimba
...
This series of supportive tools are based on the WHO Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. They are intended to provide supportive informati
...
COVID-19 infection affects all age groups including newborns, however, literature is scarce on the fetal and neonatal outcomes of babies e
...
12 May 2021. This third survey in the series shows that the COVID-19 pandemic continues to impact societies, not only in terms of health, but also social
...
The WHO COVID-19 Clinical management: living guidance contains the most up-to-date recommendations for the clinical management of people with COVID
...
The primary focus of the plan continues to be prevention, preparedness and treatment of the the Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. Central to t
...
As information about COVID-19 is rapidly evolving, it can be challenging to navigate and synthesize all of the information. The purpose of this doc
...
Recognizing the extent to which the COVID-19 outbreaks affects women and men differently is hugely important. Some preliminary data suggested that
...
10 May 2021. Manufactureres:
SK Bioscience Co. Ltd. [COVID-19 Vaccine (ChAdOx1-S [recombinant])]
Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd. [COVISHIELD™, ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Corona Virus Vaccine (R
...
The brief concludes that sustaining the continuity of EHS requires policies that ensure a whole-society and systems strengthening approach. This involves increased health care investment, community engagement, disease control regulations,
...
31 March 2021
This article is part of a series of explainers on vaccine development and distribution. Learn more about vaccines – from how they work and how they’re made to ensuring safety
...
24 May 2021; Guidance for vaccinators on how to store, prepare, draw up and administer COVID-19 vaccines Updated May 2021 · Western Cape Edition
...
As a Frontline Health Care Worker or a Vaccinator, you need to counsel pregnant women about the availability, value and precautions regarding the COVID-19
...
One of the many gender inequities in the health and care workforce that COVID-19 has exposed is around the fit
...
The updates are based on evidence emerging from the: Ongoing monitoring of the disease. Protection that the population already developed against COVID-19 through previous infection or vaccination. E
...
Guidelines on Management of COVID-19 in Kenya
recommended
It has been over a year since Kenya identified the first case of COVID-19 in the country. The Government formed the National COVID-
...
These WHO interim recommendations for use of the BBV152 COVAXIN vaccine were developed on the basis of advice issued by the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) and the evidence summary included in the background document
...
This policy paper underscores that, although children do not represent a high-risk group for direct COVID-19 fatality, the pandemic posts far-reaching secondary impacts that heighten risks to Africa
...
There is no secret to our procedure: the daily scanning of the literature helps us to stay afloat in the never-ending waves of new publications about SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-
...
Countries around the world are facing the challenge of increased demand for care of people with COVID-19, compounded by fear, misinformation and li
...
This drill package is part of a broader COVID-19 simulation exercise package, including vaccine tabletop exercises(TTX). For exercises to be most effective, it is recommended they should be
...
This guide is designed to accompany the training module, Communicating with health workers about COVID-19 vaccination. It provides detailed explanations, resources
...
Thefirst report on Latin America and the Carribean presents key indicators on health and health systems in 33 Latin America and the Caribbean coun
...
The WHO COVID-19 Clinical management: living guidance contains the Organization’s most up-to-date recommendations for the clinical management of people with
...
As of 12 December 2022, over 645 million people worldwide have been diagnosed with COVID-19, with over 6.6 million deaths (4).
The Omicron variant, which emerged in late November 2021,
...
There has been important progress for the rights of adolescent girls and women in recent decades, yet millions still struggle to
access the nutritious diets, essential nutrition services and nutrit
...
RMRP 2020 - Regional Refugee and Migrant Response Plan for Refugees and Migrants from Venezuela 2020
The Venezuelan refugee and migrant crisis is one of the biggest external displacement crises in the world today. The COVID-19 pandemic has compound
...
This quick guide offers basic information about COVID-19, the Sinovac-CoronaVac COVID-19 vaccine
...
WHO today released its first roadmap to tackle postpartum haemorrhage (PPH) – defined as excessive bleeding after childbirth - which affects millions of women annually and is the world’s leading cause of maternal deaths.
Despite being prevent
...
This guide focuses on three main areas: how to support a person whose condition warrants home care because of non-severe symptoms and home care is recommended by local jurisdictions; how to prevent the spread of
...
Oxfam’s report found that Covid-19 has the potential to increase economic inequality in almost every country at once, the first time this has happened since records began over a century ago. It se
...
The pandemic has emphasized the high risk of avoidable harm to patients, health workers, and the general public, and has identified a range of safety gaps across all core components of health system
...
Violence against women and girls is widespread in the Region of the Americas, resulting in enormous consequences for the health and wellbeing of women and
...
No education system is effective unless it promotes the health and well-being of its students, staff and community. These strong links have never been more visible
...
Constituting the second part of the World Drug Report 2022, the present booklet contains an overview of the global demand for and supply of drugs.
The first chapter of the booklet begins with the latest estimates of the number of people who use dru
...
Interim recommendations for use of the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine, CoronaVac, developed by Sinovac
These WHO interim recommendations for use of the Sinovac-CoronaVac were developed on the basis of advice issued by the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) and the evidence summary included in the background document
...
an approach to optimize the global impact of COVID-19 vaccines, based on public health goals, global and national equity,
...
These WHO interim recommendations for use of the COVID-19 vaccine BIBP produced by Sinopharm were developed on the basis of advice issued by the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (
...
WHO Guideline on self-care interventions for health and well-being, 2022 revision: executive summary
recommended
A global shortage of an estimated 18 million health workers is anticipated by 2030, a record 130 million people are in need of humanitarian assistance, and there is the global threat of pandemics such as C
...
The early prevention project “Strong together!” supports refugee parents and their young children (0–4 years) in Berlin, Germany. It aims to mitigate the transmission of trauma to the generation born in exile. For refugee families who have onl
...
First published in 2020, this toolkit is intended for clinicians working in acute care, managing adult and paediatric patients with acute respiratory infection, including severe pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis
...
6 June 2022
These WHO interim recommendations on the use of the Janssen Ad26.COV2.S (COVID-19) vaccine were developed on the basis of advice issued by the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Im
...
1 June 2020
Countries around the world are facing the challenge of increased demand for care of people with COVID-19, compounded by fear, misinformation
...
These WHO interim recommendations on the use of the Pfizer – BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine against Covid-19 were developed on the basis of advice issued by the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on I
...
These WHO interim recommendations on the use of the Astra Zeneca – Oxford University AZD1222 vaccine against Covid-19 were developed on the basis of advice issued by the Strategic Advisory Group o
...
27 September 2022
These WHO interim recommendations for use of the Novavax NVX-CoV2373 vaccine were developed on the basis of advice issued by the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) and the evidence summary included in the b
...
It is widely understood that the food insecurity crisis in the Sahel and the Horn of Africa is one of the world’s fastest growing and most neglected crises. It lacks sufficient global focus, resou
...
Updated 2022. This guide addresses the care pathway from presentation of the patient to a health facility to patient discharge. It considers different levels of disease severity, from asymptomatic individuals to critically ill patients. Accounting for variations in the benefits
...
Updated 10 August 2020
This document presents an essential medicines list (EML) to manage patients in intensive care units (ICUs) with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 diagnosis, which includes acti
...
The Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on Immunization held a meeting on 3-6 October 2022. This report summarizes the discussions, conclusions and recommendations.
It covers the following items:
Global Reports
Immunization Agenda 2030
...
This global progress report attempts to lay the groundwork for the kind of accelerated action needed. Section 1 presents key data, trends and developments in women’s, children’s and adolescents�
...
It is intended for use among clinicians taking care of moderate to severe COVID-19 cases.
The COVID-19
...
Coronavirus (COVID-19) is the illness caused by a new strain of coronavirus first identified in Wuhan city, China. It can cause a cough and/or a fe
...
Community health workers (CHWs) enable marginalised communities, often experiencing structural poverty, to access healthcare. Trust, important in all patient–provider relationships, is difficult to build in such
communities, particularly when stigma associated with HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis
...
Preliminary overview of refugees and migrants self-reported impact of COVID-19
The study surveyed over 30,000 refugees
...
What school closures under COVID-19 mean for children and young people in
crisis-affected contexts
Kenya reported its first case of COVID-19 on 12 March 2020 and, as at 7 April 2020, 172 cases had been confirmed
...
During the year 2022, COVID-19 continued to be a significant challenge in Eritrea as in many other countries across the world. As COVID-
...
Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19) was declared a global pandemic on 11 March 2020, and Malawi declared its first case on 2 April. As of 30 April, t
...
Measuring progress towards universal health coverage.
This sixth edition of Health at a Glance Asia/Pacific presents a set of key indicators of health status, the determinants of health, health care resources and utilisation, health care expenditur
...
Cognizant of the need for standardization of the response for COVID-19, the Federal Ministry of Health prepared this national guideline in an effort to contain the epidemic before it overwhelms the
...
Promoting health and preventing disease is a critical component of the effort required to achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC). to date, efforts to achieve UHC have focused mostly on strengthening health systems
...
Testing men for HIV during their partner’s pregnancy can guide couples-based HIV prevention and treatment, but testing rates remain low. We investigated a combination approach, using
...
Food and nutrition security in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is subject to the relentless impact of conflict, epidemics and climate events that have persisted in the country for decades, furt
...
Developing countries face disastrous healthcare setbacks, hunger and huge international debt as covid-19’s ‘final wave’