Filter
2075
Text search:
CAR
Featured
170
528
Language
1103
1000
61
44
37
21
17
15
8
7
6
5
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Document type
1152
365
251
77
73
56
56
19
15
6
2
2
1
Countries / Regions
138
101
82
60
60
55
42
38
35
34
32
31
31
30
28
26
25
25
23
22
22
22
21
21
19
18
17
17
15
15
13
13
12
12
11
11
11
10
10
10
9
9
9
8
8
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
124
81
69
61
55
55
48
42
41
38
36
33
26
19
19
17
15
13
13
12
12
11
11
11
10
10
10
9
9
9
9
9
8
8
7
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Publication Years
502
1372
189
11
1
Category
788
129
117
81
71
41
20
1
1
Toolboxes
207
191
103
102
75
73
67
66
66
65
56
44
30
27
24
24
20
18
15
14
11
11
3
1
1
Psychiatrie de l'enfant
Chapitre B.2
Edition en français
Traduction : Claire Rousseau
Sous la direction de : Priscille Gérardin
Avec le soutien de la SFPEADA
UNHCR, the UN Refuge Agency, and NGO partners are launching an appeal for US$2.7 billion to address the live-saving humanitarian needs of South Sudanese refugees in 2019 and 2020.
Five years on since the onset of a brutal civil war, over 2.2 million South Sudanese refugees have sought safety in six
...
neighboring countries Uganda, Sudan, Ethiopia, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and Central African Republic (CAR). Another 1.9 million remain internally displaced inside South Sudan
more
Autres troubles
Chapitre H.5
Edition en français Traduction : Bojan Mirkovic Sous la direction de : Priscille Gérardin Avec le soutien de la SFPEADA
Des efforts considérables ont été menés pour apporter aux
populations rurales du continent africain des soins de base. Mais
la qualité de ces soins reste aujourd’hui peu satisfaisante car le
médecin généraliste est le plus souvent absen
...
t en première
ligne. Cette situation est paradoxale en regard du nombre de
médecins formés dans les facultés en Afrique francophone et à
Madagascar. Le déficit en médecin généraliste, exerçant dans les
zones rurales, reste particulièrement préoccupant alors que
les jeunes médecins sans emploi se multiplient dans les villes.
L’ONG Santé Sud, depuis plus de vingt ans, propose un concept
– la médecine générale communautaire – qui, associé à un dispositif
d’accompagnement, a permis l’installation de plus de deux
cents médecins généralistes communautaires au Mali et à
Madagascar. Ce concept a pour intérêt d’associer, dans une même
pratique, la médecine de famille et les Soins de Santé Primaires.
S.F.S.P. | « Santé Publique »
2014/HS S1 | pages 59 à 65
Considerable effort has been made to provide rural African
populations with basic health care, but the quality of this care
remains unsatisfactory due to the absence of first-line GPs. This is
a paradoxical situation in view of the large number of physicians
trained in medical schools in French-speaking Africa and
Madagascar. of the lack of GPs working in rural areas is a real
concern, as many young doctors remain unemployed in cities.
For more than 20 years, the NGO Santé Sud has proposed a
Community General Medicine concept, which, combined with
a support system, has allowed the installation of more than
200 community GPs in Mali and Madagascar. The advantage of
this concept is that it provides family medicine and primary health
care in the same practice.
S.F.S.P. | « Santé Publique »
2014/HS S1 | pages 59 à 65
more
Le cancer du col de l’utérus et le cancer du sein constituent de véritables problèmes de santé publique en raison de leur fréquence. A titre d'exemple, environ 275 000 femmes meurent chaque année d’un cancer du col de l’utérus dans le monde et la plupart de ces décès surviennent dans
...
des pays à revenu faible (90%) car le diagnostic est souvent fait à des stades avancés de la maladie.
more
La pandémie actuelle de COVID-19 entraîne des difficultés exceptionnelles et sans précédent pour les autorités compétentesa responsables des systèmes nationaux decontrôle de la sécurité sanitaire des alimentsb, qui sont tenues de continuer à assurer des fonct
...
ions et des activités de routine en se conformant aux règlements nationaux et aux recommandations internationales. Dans de nombreux pays, le personnel employé par les autorités compétentes travaille généralement à domicile car le télétravail est devenu la norme et toutes les réunions en présentiel sont annulées ou sont réorganisées sous forme de téléconférence. Il est difficile de maintenir, sans interruption, les activités de routine telles que l’inspection des entreprises du secteur alimentaire, la certification des exportations, le contrôle des denrées alimentaires importées, le suivi et la surveillance de la sécurité de la chaîne d’approvisionnement alimentaire, l’échantillonnage et l’analyse des aliments, la gestion des incidents alimentaires, les conseils sur la sécurité sanitaire des aliments et la réglementation relative aux denrées alimentaires à l’intention de l’industrie et la communication au grand public sur les questions relatives à la sécurité sanitaire des aliments.
more
Le Bénin est un pays à épidémie mixte car il existe des poches de concentration de fortes prévalences
au sein de certaines populations clés plus exposées aux risques d’infection, notamment les TS et
leurs partenaires, les prisonniers, les
...
HSH et les UDI. Les sections suivantes présenteront la
prévalence dans les différents groupes.
more
La santé est un droit humain universel et un facteur essentiel de bien-être, de développement économique, de croissance,
de richesse et de prospérité pour tous. Les systèmes de santé jouent un rôle essentiel, car ils protègent, rétabliss
...
ent et
préservent la santé des patients et des populations. Un personnel de santé bien formé, motivé et soutenu est la clé de
voûte de tout système de santé et, sans lui, il n’y aurait pas de soins de santé
more
Ce profil pays est le résultat d'une évaluation du paysage menée par le personnel et les collègues d'Advancing Partners & Communuties (APC). Cette évaluation du paysage portait sur les pays prioritaires de l'Agence des États-Unis pour le Développement International (USAID) en termes de Popula
...
tion et de Santé de la Reproduction, et s'intéressait plus particulièrement à la planification familiale car c'est le point central du projet APC. Le but de l'évaluation du paysage fut de recueillir les informations les plus récentes disponibles sur le système de santé communautaire, les agents de santé communautaires et les services de santé communautaires dans chaque pays. Ce profil est destiné à refléter les informations recueillies. Lorsque cela est possible, les informations présentées sont justifiées par les politiques nationales et d'autres documents pertinents ; cependant, une grande partie des informations sont le résultat de l'expertise institutionnelle et d'entrevues personnelles en raison de l'absence relative d'informations publiquement disponibles sur les systèmes nationaux de santé communautaires. En conséquence, des lacunes et des incohérences peuvent exister dans ce profil.
more
Introduction
Chapitre A.2
Edition en français
Traduction : Lisa Vitte, Anne-Sophie Perrin
Sous la direction de : Priscille Gérardin Avec le soutien de la SFPEADA
Integrating trauma healing for partner staff into recovery programming.
This assessment shares testimonies from CRS and partner staff who participated in a trauma healing program in Central Africa Republic.
CRS's trauma-healing methodology uses small groups—of all genders, ages and faiths—focu
...
sing on the survivors of violence. Religious leaders, members of community protection committees, and local authorities also participate in these groups. Basic trauma‑healing workshops focus on individual sharing and healing while laying the foundation for communities to build capacity to respond to widespread suffering
more
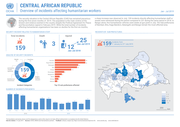
The security situation in the Central African Republic (CAR) has remained precarious during the first seven months of 2019. The population is the main victims of the tension and violence exerted in the country despite the Political Agreement for Pea
...
ce and Reconciliation signed in February 2019. While the total number of incidents affecting humanitarian organizations has been on decline for the first six months, a sharp increase was observed in July. 159 incidents directly affecting humanitarian staff or assets were witnessed during the period compared to 231 during the same period in 2018. In Bangui alone, five humanitarian vehicles were stolen at gun point in July. The Sub-prefectures of Bambari, Bria, Kaga-Bandoro, Batangafo and Bangui remain the most affected area
more
Vous avez une infection confirmée mais vous ne devez pas être hospitalisé car votre état général est bon. Vous devez néanmoins être isolé à domicile. Les personnes vivant sous le même toit et vos relations intimes doivent se mettre en aut
...
o-quarantaine pour une période de 7 jours. Ces recommandations vous disent quelles précautions vous et votre entourage devez prendre pour limiter la transmission du virus.
more
Children and youth can face emotional strains after a traumatic event such as a car crash or violence. Disasters also may leave them with long-lasting harmful effects. When children experience a trauma, watch it on TV, or overhear others discussing
...
it, they can feel scared, confused, or anxious. Young people react to trauma differently than adults. Some may react right away; others may show signs that they are having a difficult time much later. As such, adults do not always know when a child needs help coping. This tip sheet will help parents, caregivers, and teachers learn some common reactions, respond in a helpful way, and know when to seek support.
more
After a frightening or distressing experience (any kind of injury, a physical or sexual assault, car crash, fire, or other natural disaster), a child or teen may suffer psychological
stress in addition to any physical injuries.
When these reaction
...
s last for more than a month and are strong enough to affect a child's or teen's everyday functioning, that child may be diagnosed as having Post- Traumatic Stress Disorder or PTSD.
more
Accessed on 29.01.2020
Malgré la disponibilité des services de soins dans les structures sanitaires il existe des problèmes liés à l’accès aux soins dans certaines zones.
Car la plupart des sujets les plus exposés au paludisme: hor
...
s de portée des structures de santé et l' accès limité au diagnostic et au traitement.
D’où stratégie Prise En charge des CAs de paludisme à DOMicile: PECADOM
more
Ce document met en évidence nos objectifs stratégiques, nos pays prioritaires et nos besoins de financement pour les six premiers mois.
COVID-19 est une crise sans précédents. L’impact sur les filles et les garçons que nous soutenons est potentiellement dévastateur,
...
car ceux qui protègent et s’occupent des enfants succombent à la maladie et les services essentiels sont interrompus. Cette crise affecte la vie de nos donateurs, de notre personnel et de nos proches. Pourtant, comme en de nombreuses occasions dans notre histoire, c’est en période de crise que Vision Mondiale révèle son meilleur potentiel.
more
Travailler avec les dirigeants communautaires pour lutter contre la VBG est une très bonne et prometteuse approche, car les dirigeants communautaires sont les gardiens de toutes nos croyances et coutumes. Étant donné que la VBG est enracinée
...
dans les croyances et les coutumes, essayer de s’attaquer à la VBG sans impliquer les dirigeants communautaires peut mener à un grand conflit, et vous n’aurez aucun résultat. Les dirigeants communautaires ont également des rôles à jouer dans la réponse aux survivantes de la VBG. Les survivantes s’adressent aux chefs de villages pour faire part de leurs préoccupations et de leurs expériences, et les dirigeants ont des pratiques pour traiter les préoccupations et une approche de la justice qui se base d’abord sur le maintien de la cohésion sociale, mais la VBG ne peut pas être résolue comme n’importe quel autre conflit. D’après mon expérience des programmes de VBG dans mon propre pays et ailleurs, j’ai appris qu’il est plus difficile d’impliquer les dirigeants communautaires dans certains endroits que dans d’autres. Parfois, les aspects religieux rendent les choses plus difficiles. Mais si vous demandez à n’importe quel dirigeant de décrire ce qu’est un dirigeant, ce qu’un dirigeant fait, il parlera de la protection de la communauté. Et c’est aussi ce que nous voulons — protéger les femmes et les filles dans la communauté.
more
• Clashes continued between the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), the Syrian Arab Army (SAA), and Turkish backed forces, concentrated around the M4 highway and Tal Tamer district in Al-Hasakeh. Further displacement was reported.
• Several civilian casualties occurred due to improvised explosive
...
devices (IEDs) in Afrin, Quamishli, and along the Tell Abiad-Ras al-Ain corridor. On 16 November, a car bomb in Al Bab, Aleppo reportedly killed 14 people and injured 27, including civilians.
• On 13 November, Alouk water station was repaired following reconnection of the Debarseyah supply line, again restoring water to 460,000 people in Al-Hasakeh city and surrounding areas
more