Filter
4091
Featured
464
923
Language
Document type
2354
627
467
222
123
113
78
33
29
28
11
4
1
1
Countries
226
134
114
107
106
87
80
79
71
70
68
61
58
57
56
51
50
48
48
42
41
40
40
35
34
31
30
28
28
25
25
25
23
22
22
22
21
19
19
19
18
18
16
16
16
13
13
12
12
12
12
11
11
11
10
9
9
9
9
8
8
8
8
8
7
7
7
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
1627
294
241
166
102
99
47
1
Toolboxes
730
474
284
279
139
123
107
97
80
73
63
63
56
44
44
23
23
22
21
12
12
11
8
A Consumer Guide
Printed 2006
Revised 2007, 2008, 2011, 2014, and 2015
The environment in which young people live, learn and play significantly affects their decisions about whether to consume alcohol. Environmental factors are the main risk factors driving alcohol con
...
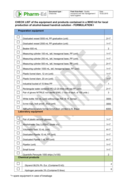
Protocol for the management of specialized centres for the treatment of people with alcohol and other drug abuse problems (CETAD) in the framework of the COVID-19 pandemic. Version 1.
Background
The core clinical symptoms of addiction include an enhanced incentive for drug taking (craving), impaired self-control (impulsivity and compulsivity), emotional dysregulation (negative mood) and increased stress reactivity. Symptoms related to impaired self-control involve reduced activi
...
The manual is written for clinicians working at the district hospital (first-level referral care) who diagnose and manage sick adolescents and adults in resource constrained settings. It aims to support clinical reasoning, and to provide an effective clinical approach and protocols for the managemen
...
Alcohol, medication, tobacco, illegal drugs, addictive behaviour
Second, revised edition with new layout
Juni 2014
Alcohol misuses
Substance use disorders
Chapter G.1
УСПЕХИ В РЕАЛИЗАЦИИ ПОЛИТИКИ В ОТНОШЕНИИ КОНТРОЛЯ НАД АЛКОГОЛЬНОЙ ПРОДУКЦИЕЙ, 2010–2019 ГГ
A detailed overview is provided of the implementation of alcohol policies described
...
A tool for measuring alcohol policy implementation
WHO Western Pacific Regional Strategy to Reduce Alcohol-Related Harm
Монографія має за мету ознайомити громадськість із проектом ESPAD – Європейське опитування учнів щодо вживання алкоголю та інших наркотичних речовин (European School Survey Pr
...
In this entry we are looking at smoking, alcohol consumption and the use of illicit drugs. We are studying who is using these substances, how their use has changed over time, and we are presenting the estimates of their impact on health. Collectivel
...
Documento incluye recomendaciones para personas con necesidades de manejo terapéutico asociados a consumo problemático de alcohol y otras drogas, problemas o enfermedades de salud mental, discapacidad psíquica, o en condiciones de exclusión soci
...
The manual contains basic principles of prescribing followed by chapters on medicines used in psychotic disorders; depressive disorders; bipolar disorders; generalised anxiety and sleep disorders; obsessive-compulsive disorders and panic attacks; and alcoh
...
The publication conveys the most recent quantitative surveillance results focusing on noncommunicable disease (NCDs)-related risk behaviours among adults from the WHO STEPwise approach to NCD risk factor surveillance (STEPS) and tobacco use among adults from the Global Adult Tobacco Survey (GATS) in
...
The publication conveys the quantitative surveillance results focusing on tobacco use and noncommunicable disease (NCD) related behaviours among youth (13–15 years) in Member States of the WHO South-East Asia Region, namely, the Global School-based Student Health Survey (GSHS) and the Global Youth
...
Poverty, HIV and other disease burdens, coupled with common mental disorders including alcohol and other substance use disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder, clinical and postnatal depression, distress, and anxiety, impact how caregivers meet the
...
his manual is for people who have had no formal training in counselling but wish to learn the necessary components to establishing an effective counselling relationship. It will be useful for anyone who is involved in counselling people with a mental health problem.
h
...
If you are healthy, you only need to wear a mask if you are taking care of a person with suspected 2019-nCoV infection.
Wear a mask if you are coughing or sneezing.
Masks are effective only when used in combination with frequent hand-cleaning with
...
Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Jul [date cited]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2607.200915
Infection control instructions call for use of alcohol-based hand rub solutions to inactivate severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. We determined the virucid
...
Hand Hygiene and COVID-19
recommended
MEDBOX Issue Brief No.2.
The main route of transmission of the Sars-CoV-2 virus are small respiratory droplets. Therefore, thoroughly cleaning of hands with either alcohol-based hand rub or soap and water is one of the corner stones of basic protec
...
Best practice for hand hygiene requires the availability of clean water, soap, and single use disposable towels or alcohol based hand sanitiser with a concentration of 70%. Availability of these resources is not always assured. When resources for ha
...
El agente etiológico de la tuberculosis es el Mycobacterium tuberculosis o bacilo de Koch. Se trata de un bacilo aerobio estricto, ácido-alcohol resistente, sin movilidad, de crecimiento lento y que se inactiva con rayos ultravioleta y temperatura
...
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a condition which generally has no symptoms and if left untreated, can lead to heart attacks, heart failure, stroke, kidney failure and blindness. Risk factors include older age, overweight or obesity, lack of physical activity, high salt/sodium intake, and h
...
The risk factors for CVD include behavioural factors, such as tobacco use, an unhealthy diet, harmful use of alcohol and inadequate physical activity, and physiological (metabolic) factors, including high blood pressure (hypertension), high blood ch
...
The Federal Centre for Health Education (BZgA) emphasizes the critical role of drug prevention in enhancing public health in Germany. Annually, the country faces significant premature mortality due to substance use: at least 110,000 deaths from smoking, 40,000 from harmful
...
The new guide provides practical, first-line management recommendations for mental, neurological and substance use conditions. Contents include modules on assessing and managing conditions such as acute stress, grief, moderate-severe depressive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, epilepsy, and
...
The "Global NCD action plan" provides a road map and a menu of policy options for countries to take in order to attain the 9 voluntary global targets, including that of a 25% relative reduction in premature mortality from cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes or chronic respiratory diseases by 2
...
Contains many illustrations of all country materials – of risk factors, treatment procedures, side effects, coping, healthy lifestyle, and more; Promotes cancer screening, especially for breast and cervical cancer, and gives local resources; Educates about local cancer risk factors, e.g., HIV infe
...
This report examines how urban living affects residents’ mental health and happiness, and ways to use this information to create saner and happier cities. Some often-cited studies suggest that urban living increases mental illness and unhappiness, but a critical review indicates that much of this
...
Mental health conditions affect one in 10 people at any one time and account for a large proportion of non-fatal disease burden. There is a high degree of comorbidity between mental health conditions such as depression and other noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), including cardiovascular disease, diab
...
This booklet presents data on NCD mortality and prevalence of NCD risk factors, by country, for the Region of the Americas. The focus is on the 5 x 5 NCD agenda which includes the main NCDs (cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases), and mental health (suicide); as
...
Este folleto presenta los datos sobre la mortalidad por ENT y la prevalencia de factores de riesgo de las ENT, para los países en la región de las Américas. Su contenido está enfocado en la agenda 5 x 5 de ENT que incluye las principals ENT (enfermedades cardiovasculares, cáncer, diabetes y enf
...
The ten mythbusters, available in English and Siswati, were developed based on feedback received from chiefdom leadership who identified prevailing myths and misconceptions related to COVID-19 prevention, treatment or stigma related to recovery.
Key mythbusters tackle use of
...
The Government of the Republic of Zambia has placed priority on ensuring that Zambians are healthy and productive as a catalyst to the attainment of socioeconomic development . The Vision 2030 aims to transform Zambia into a prosperous middle-income country as articulated also in the 7th National De
...
В данном бюллетене приведена важная информация относительно COVID-19
и употребления алкоголя, которой необходимо владеть. Также, особое внимание
уделено дезинформа�
...
More than 700 000 people lose their life to suicide every year. The world is not on track to reach the 2030 suicide reduction targets. WHO advocates for countries to take action to prevent suicide, ideally through a comprehensive national suicide prevention strategy. Governments and communities can
...
Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) are the principal cause of morbidity, disability and premature mortality in Azerbaijan. The most effective way to reduce the NCD burden is to prevent NCD development, by addressing thebehavioural risk factors underlying NCDs at the population and individual leve
...
This document summarizes the findings of the STEPS survey in Ukraine and compares them with the results of STEPS surveys carried out in other countries in the WHO European Region, as well as with selected other surveys in Ukraine. The survey is designed to be repeated approximately every five years
...
Risk factors for noncommunicable diseases in Ukraine in 2019. This document summarizes the findings of the STEPS survey in Ukraine and compares them with the results of STEPS surveys carried out in other countries in the WHO European Region, as well as with selected other surveys in Ukraine. The sur
...
During the first year of the Covid-19 pandemic, the world’s economy slowed. Yet, the global annual average particulate pollution (PM2.5) was largely unchanged from 2019 levels. At the same time, growing evidence shows air pollution—even when experienced at very low levels—hurts human health. T
...
Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) are responsible for 81% of all deaths in the region of the Americas, of which 34% befall prematurely in people between 30- 69 years old. The burden of theses diseases and their common risk factors jeopardize the health systems to provide adequate management, as well a
...
Tanzania, like other developing countries, is facing a higher burden of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). The country is experiencing rapid growth of modifiable and intermediate risk factors that accelerate CVD mortality and morbidity rates. In rural and urban settings, cardiovascular risk factors suc
...
Cardiovascular diseases, principally ischemic heart disease (IHD), are the most important cause of death and disability in the majority of low- and lower-middle-income countries (LLMICs). In these countries, IHD mortality rates are significantly greater in individuals of a low socioeconomic status (
...
Key facts
- Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death globally.
- An estimated 17.9 million people died from CVDs in 2019, representing 32% of all global deaths. Of these deaths, 85% were due to heart attack and stroke.
- Over three quarters of CVD deaths take place in low- an
...
The World Health Organization's fact sheet on hypertension provides a comprehensive overview of high blood pressure, highlighting its prevalence, risk factors, and health implications. It emphasizes that hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide, with an estimated 1.28 billion adult
...
The pamphlet "ADHD Medications" provides an overview of medications commonly used to treat ADHD, such as Adderall, Vyvanse, and Ritalin. It explains that these medications do not enhance intelligence and affect individuals differently based on dosage and medical history. Potential dangers of misuse
...
The "Global NCD action plan" provides a road map and a menu of policy options for countries to take in order to attain the 9 voluntary global targets, including that of a 25% relative reduction in premature mortality from cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes or chronic respiratory diseases by 2
...
The Noncommunicable Diseases Country Profiles 2018 by the World Health Organization (WHO) provides an in-depth look at the burden of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes across WHO Member States. It includes data on NCD m
...
The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) provides comprehensive information on noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), including cardiovascular diseases, cancers, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases. The website emphasizes that NCDs are the leading cause of death and disability globally, accounti
...
The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) provides comprehensive information on noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), including cardiovascular diseases, cancers, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases. The website emphasizes that NCDs are the leading cause of death and disability globally, accounti
...
The World Health Organization's fact sheet on noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) highlights that NCDs, such as cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes, are responsible for 74% of all global deaths, totaling 41 million annually. Notably, 86% of premature NCD deaths (
...
The "Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases 2013-2020," published by the World Health Organization (WHO), provides a roadmap to reduce premature deaths from noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) like heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. It emphasizes strengthening he
...
The "Global mapping report on multisectoral actions to strengthen the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) and mental health conditions" by the WHO provides insights into how different countries are implementing multisectoral approaches to address NCDs and mental health issues.
...
Chronic noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) are the number one cause of death and disability in the world. The term NCDs refers to a group of conditions that are not mainly caused by an acute infection, result in long-term health consequences and often create a need for long-term treatment and care. The
...
Chronic noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) are the number one cause of death and disability in the world.
The term NCDs refers to a group of conditions that are not mainly caused by an acute infection, result in long-term health consequences and often create a need for long-term treatment and care.
...
Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) or Chronic noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) are the 1st cause of death and disability worldwide.
The term NCDs refers to a group of conditions that are not mainly caused by an acute infection, result in long-term health consequences and often create a need for long-
...
Psychoactive drugs are substances that, when taken in or administered into one's system, affect mental processes, e.g. perception, consciousness, cognition or mood and emotions. Psychoactive drugs belong to a broader category of psychoactive substances that include also
...
This dataset contains data from WHO's data portal covering the following categories:
Air pollution, Antimicrobial resistance (AMR), Assistive technology, Child mortality, Dementia diagnosis, treatment and care, Dementia policy and legislation, Environment and health, Foodborne Diseases Estimates,
...
A case study from Albania
June 2016
EHRN is grateful to all who contributed to this document, especially (in alphabetical order): Alena Alba, Program Officer, Eastern Europe and Central Asia Team, Asia, Europe, Latin America and the Caribbean Department, The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberc
...
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) pose a substantial threat to many health systems, especially in low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs) where they are already overstretched. In the past few decades, deaths from NCDs in LMICs have spiked, whereas numbers in high-income countries have stabilis
...
ATLAS on substance use (2010) — Resources for the prevention and treatment of substance use disorders
Accessed: 14.03.2019
Esta ficha informativa destaca a relação entre o consumo de álcool e a COVID-19. O consumo episódico pesado é considerado um risco à saúde para a COVID-19, e o álcool é usado por alguns para lidar com as emoções difíceis que aumentaram durante a pandemia.
Schools are generally the most popular setting for drug-use-
prevention programmes, and are used both by governmental and
non-governmental agencies. This may be for many reasons: ease of
obtaining funding for school drug-use-prevention programmes, the
captive audience, and the popular perception
...
Это учебное пособие содержит информацию о том, как спланировать обучение и содействовать работникам первичного звена медико-санитарной помощи с тем, чтобы они мог
...
Европейскому региону ВОЗ принадлежит незавид-ное первенство среди регионов мира по количеству потребляемого алкоголя и масштабам вреда, обусловленного употребл�
...
ATLAS on substance use (2010)— Resources for the prevention and treatment of substance use disorder
Accessed: 14.03.2019
ATLAS on substance use (2010) — Resources for the prevention and treatment of substance use disorders
Accessed: 14.03.2019
Куріння, вживання алкоголю та наркотичних речовин серед підлітків, які навчаються: поширення й тенденції в Україні : За результатами дослідження 2015 року в рамках м�
...
Основна мета підготовки цієї монографії – ознайомити українське суспільство з рівнем поширення серед підлітків тютюнокуріння, вживання алкоголю, наркотичних ре�
...
Accessed: 28.03.2019
Злоупотребление алкоголем и алкоголизм относятся к ведущим причинам ухудшения здоровья и повышения смертности населения. Чрезмерное употребление алкоголя служи
...
El presente manual trata de proporcionar información sencilla, adecuada y basada en datos
científicos a los prestadores de servicios de salud, especialmente en los países de ingresos bajos y medios, para que puedan administrar tratamientos farmacológicos a las personas con trastornos mentales.
...
ATLAS on substance use (2010) — Resources for the prevention and treatment of substance use disorders
Accessed: 14.03.2019
Hand Hygiene: Why, How and When?
recommended
Hand Hygiene: Why, How, & When?
MICS surveys measure key indicators that allow countries to generate data for use in
policies and programmes, and to monitor progress towards the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and
other internationally agreed upon commitments.
Accessed 14 July 2015
Accessed 3rd of October 2015
Accessed: 22.03.2019
JOURNAL OF THE ASSOCIATION OF NURSES IN AIDS CARE, Vol. 28, No. 2, March/April 2017, 186-198
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jana.2015.09.003
World Health Organization - Cancer Country Profiles, 2014.
Policy Brief | April 2015 | This brief accompanies the data sheet, Addressing Risk Factors for Noncommunicable Diseases Among Young People in Africa: Key to Prevention and Sustainable Development, and its data appendix, which provide all available country-specific data on four key NCD risk factors a
...
The Rwandan Ministry of Health recognizes the threat that Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) pose to health and development in Rwanda and in 2009 articulates strategies to respond to them in the Health Sector Strategic Plan 2012 - 2018 (HSSP3). Among other things, the plan calls for a national prevale
...